This post’s topic is graphene. It is one of carbon’s allotropic forms and promises to cause a technological revolution due to it’s properties.
Graphene comes from graphite. This ore have been a post’s subject.
Structure and properties
Graphene is a graphite layer formed by carbon atoms which form hexagons.

This material is transparent, elastic, flexible, electricity conductor, two-dimensional and with one atom thickness.

Why graphene is a great conductor? Carbon atom has 6 electrons: 2 in inner layer K in orbital 1s and 4 in external valence layer L. In normal state, 2s orbital is completed with two electrons and can share the other two. However, in excited state, an electron goes to higher energy 2p orbital and has 4 valence electrons.

In graphene, each carbon atom share 1 valence electron with each one of three neighbors, making sigma (\sigma) connections. 1 from s orbital and 2 from p orbital are shared, creating sp2 hybridization.
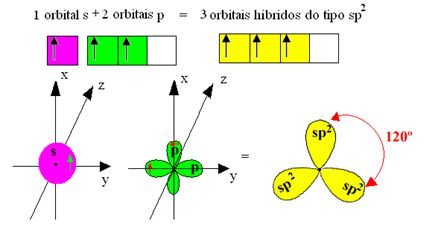
The forth electron of pure p or π orbital is above or below carbon atoms plane. This is the available electron for electricity conduction. Graphene does not have energy gap which separates valence and conduction bands.

Other physicochemical properties:
- Fracture strength of 130 GPa (Gigapascals), 100 times higher than steel, due to strong sp2 bonds.
- Young module or elasticity module is 1 TPa or 1000 GPa, indicates resistance to elastic deformation.
- Thermal conductivity: Some sources claim 3000 W/mK and others 5000 W/mK.
- Area/mass rate of 2600 m^2/g.
- Current capacity: 1\cdot 10^8 A/cm^2.
- Electric charge mobility: 200,000 cm^2/(V\cdot s).
Some application examples
- Transparent and flexible screens: Graphene’s flexibility and conductivity allow the creation of flexible screens for smartphones, computers and tablets.

These screens can be put in windows and contact lens to show contend and information.

- Filter: The thin thickness of graphene allow passage of water, but block many molecules, including sodium chloride (NaCl). A graphene based filter can be used to filter water and be used in desalination plant.

- Energy storage: Conductivity, thickness, electric charge mobility and high area per mass make possible the creation of batteries and supercapacitors more efficient, lighter and with higher capacity. Some companies already launched batteries with graphene.

- Photovoltaic panels: Flexibility, transparence and electric charge mobility higher than silicon, allow production of flexible solar panels with transparent electrodes or substrate.

- Semiconductors: Higher conductivity can increase speed of transistors and processors.
- Painting: An ink with graphene can protect a structure from mechanical stress, corrosion, heat and humidity.



