The hydroinformatics is a multidisciplinar branch which applies information technology, artificial intelligence and computer modeling to management of water resources.
Why hydroinformatics?
Water is a valuable resource which can`t be neglected. Advances in information technology allowed to create models and simulations of water mass with numeric methods of hydrodynamics, hydraulics and applied mathematics. The efficient management of water resources and aquatic ecosystems requires deep knowledge of system`s behavior. To obtain this knowledge, it`s necessary to make collection, measurement and interpretation of data to decide the best strategy in management.
Water simulation can be used to predict natural disasters like drought and flood. In addition to simulate anthropic influence in ecosystems. Exist the urban hydroinformatics, applied to water movement in sewer systems, water supply and other urban areas.
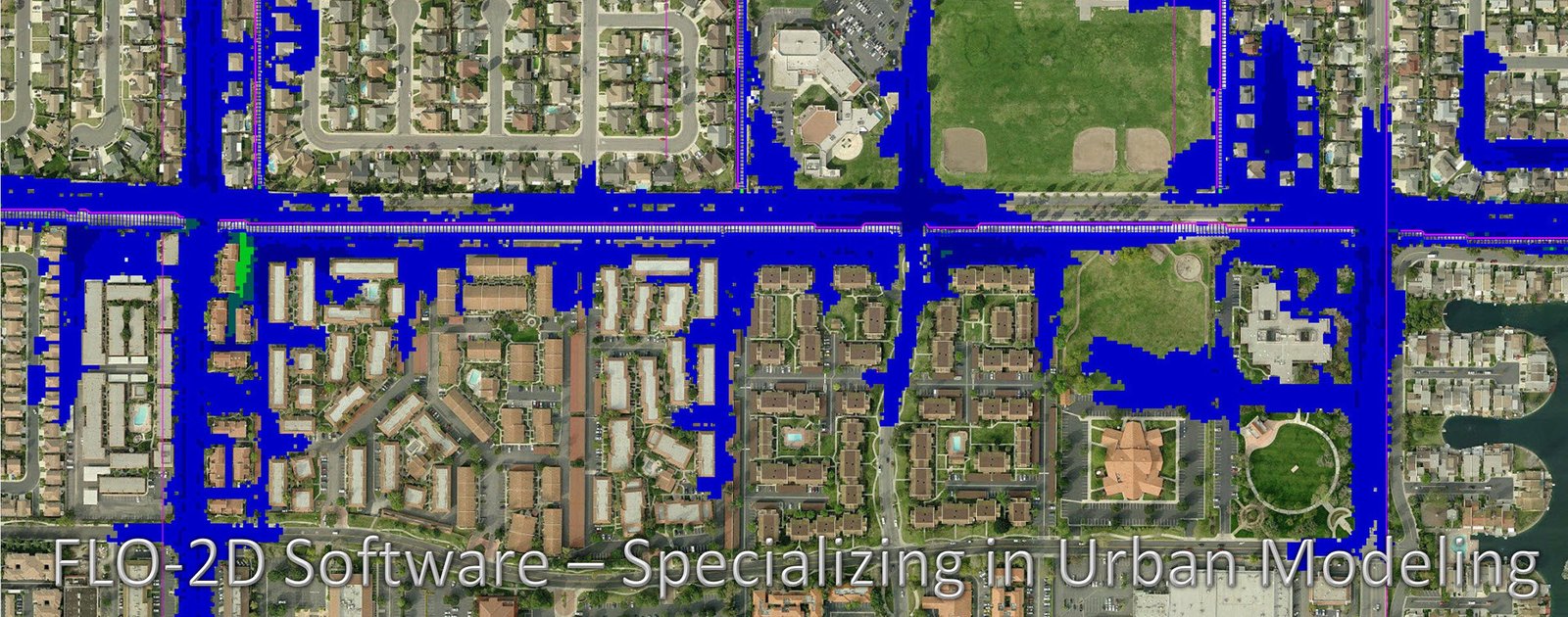
Some hydroinformatics tools
MOHID
A model is a simplified description of a real system or process. Whose functions are to improve the understanding of real domain and make predictions. MOHID is tridimensional modeling tool in ANSI Fortran 95 language. Simulates physical, chemical and biological processes of water volumes in basins, oceans, estuaries, reservoirs, etc. The gif below is a simulation of oil leaking in shore, using MOHID Water.
[WPGP gif_id=”16441″ width=”600″]
MOHID Land simulates water volumes in land. Following is a simulation of Tagus river’s flood.
[WPGP gif_id=”16443″ width=”600″]
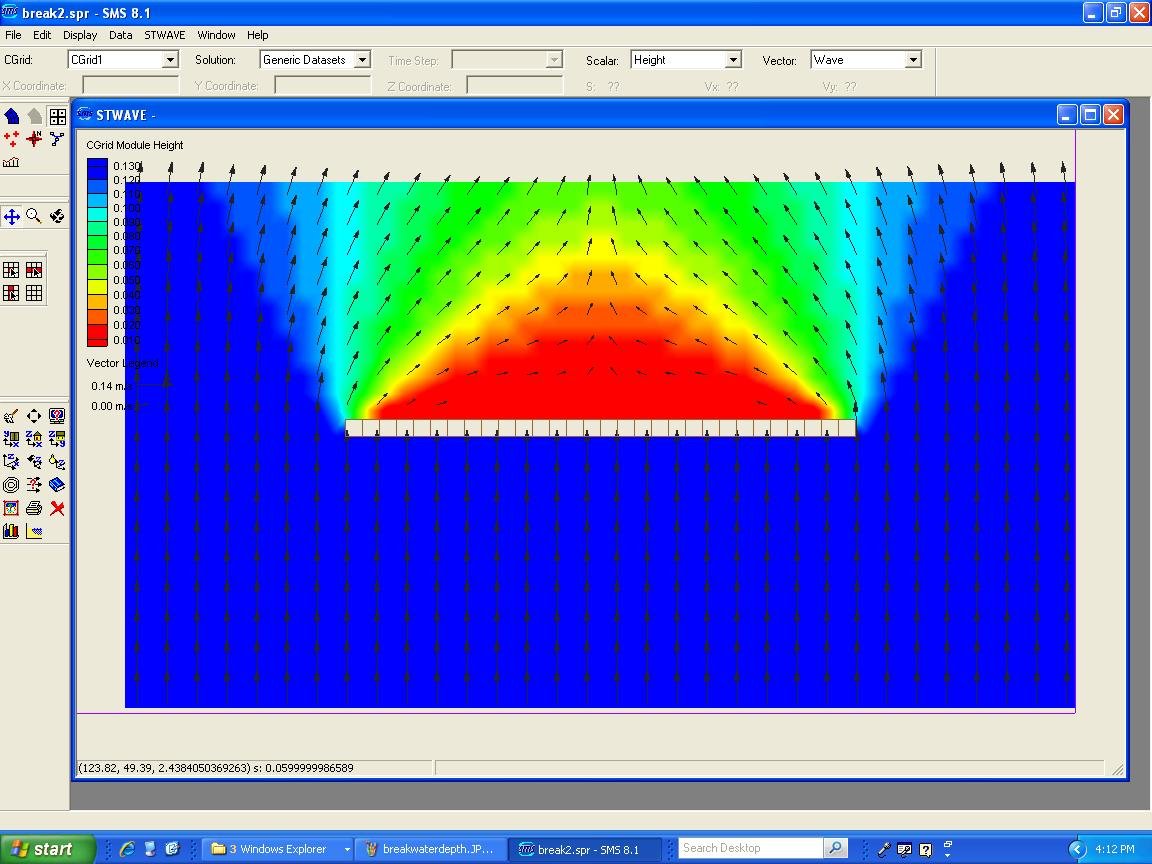
STWAVE
This is a steady-state and spectral model based software. Simulates formation and propagation of sea waves. Describing variations of wave parameters (height, period, direction and spectral form) for all trajectory until the shore. It is also possible to model wave generation by winds, diffraction, refraction, interaction between waves, etc.
AI use examples
Artificial intelligence can be used to create models and simulations based on data collection. Some examples are:
- Artificial neural networks can create rainfall-runoff models.
- Fuzzy logic in groundwater analysis.
- Fuzzy logic and neural networks to water management control.
- Flood alert using natural language processing and disaster ontologies.
Internacional Center for Hydroinformatics of Itaipu Binacional
Was built in partnership with International Hydrologic Program (IHP) of UNESCO. It is in Itaipu Technological Park (ITP) and develop innovative solutions and hydroinformatics tools to sustainable management of water resources.

Expertise areas are:
- Water and Management: Development of environmental projects, monitoring of basins and model use for groundwater, rivers and reservoirs.
- Water and Community: Education in water resources sustainability, training in environmental education, community communication and journalism.
- Water and Technology: Development of information technology in free software to basin management, availability of information for study and simulation of renewable energy and water resources.
- Water and Energy: Identification of energetic potential related to renewable energy and water sustainability, provision of subsidies for public policy and spread of better socio-environmental practices.



Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!