The Geographic Information System (GIS) serves to provide topographic information of a region to help in planning and management of natural resources, territorial and urban planning.
What is it?
It is a system which manipulates, analyzes, stores, collects and represents information of geographic space. Presents maps, satellite images, tables, graphics and topographic charts.
Components

- Software: Computational tools to store, analyze and show geographic information.
- Hardware: Computers to run softwares; peripherals like scanners, printers; in addition to networks, satellites and sensors.
- Data: Information about attributes with spatial reference and images in vector and raster, the latter are squares which remind pixels.
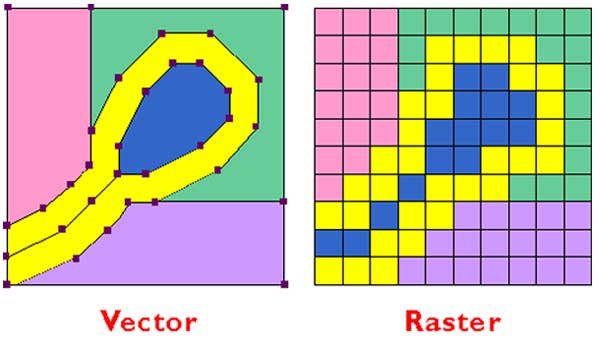
- Specialists: Qualified people manage the GIS, apply many functions and make plans.
- Methods: Procedures and applications set to achieve determined goals.
GIS tools
Remote sensing
It is the technology to obtain information from a target, can be an object, phenomena or area, without the sensor be in direct contact. In GIS, satellites and aircraft with radars and cameras which see light in wavelength beyond visible light, are used to get images from Earth’s surface. Obtained information by satellite or aircraft are retransmitted to a ground station.

Photogrammetry
Uses the principle that each eye has a different perspective about the same target and, superposition of visions produces a relief sensation. A group of aircrafts take many photos which overlap each other.
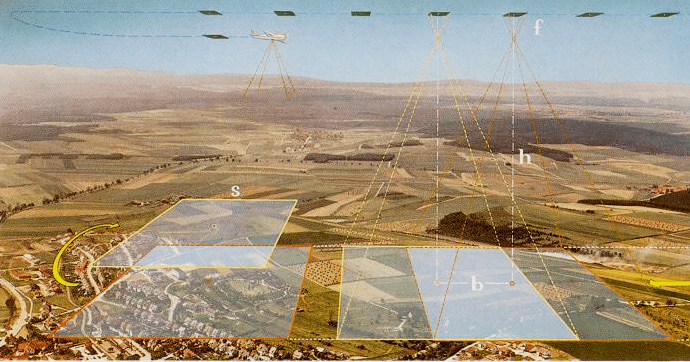
Digital stereoscopy produces an image with relief from superposition between air photos.

GPS
GPS can determine an object’s coordinates and measure it’s speed. To know how GPS works, click in button below.
Layers model
Geographic Information System divides information sets in layers. These layers can be images in vectors or bitmaps. The layers model facilitates localized problem’s identification and avoid negative impacts.

Application examples
- Delimits hydrographic basin to study about viability of hydropower plant installation.
- Monitoring of environmental protection areas.
- Urban infrastructure planning.
- Preparation for natural disasters.
- Design and implementation of telecommunication networks.



