QR code is used by many companies to catalog products, store and offer information. But how it works? Let’s find out in this post.
What is QR code?
QR means quick response. It is a two-dimensional barcode and was created in 1994 in Japan by Denso Wave company, a subsidiary of Toyota, with the proposal to catalogue automobile parts. QR code can store text, numbers, coordinates, alphanumeric digits, Japanese alphabet letters and URLs (links to websites).
Comparison with barcode
The barcode stores information in black bars with various widths with numbers below, has only one dimension.

- Extra dimension allows QR code to have more information storage capacity than barcode. For exemple, a QR code have maximum capacity of 7093 numbers. While barcode can save between 10 and 43, depends on type.
- Barcode needs to be read with a scanner which emits a light, information is read and transferred to a computer. While QR code can be read with any device which have a camera and an applicative.
- Quick response code has fault tolerance, can be scanned even damaged to a certain point. In opposition to barcode, which becomes unreadable with any damage.
Interpreting the drawing
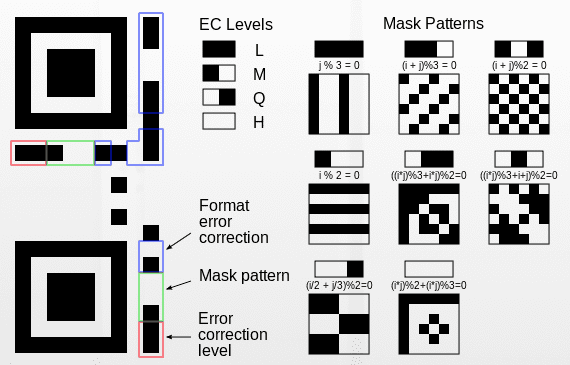
What these squares and pixels mean? The three big squares serve to identify and position the code for reader.
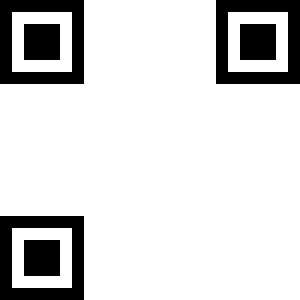
The smaller square in other corner has the finality of alignment. With this element, reader can read the drawing even inclined.
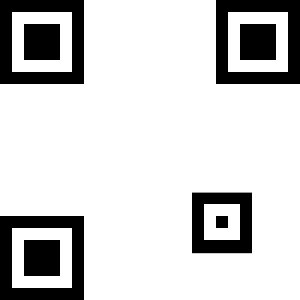
Some types of QR code need more alignment squares.
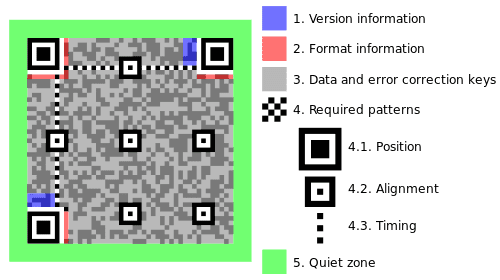
Around must have the called “quiet zone” 4 pixels wide, yellow in figure below. It’s an empty space to reader differentiate code from a background image.

Inside code, around three position squares, must be an empty space with 1 pixel width. Around this space, there are information about version and format. Version, blue in figure above, indicates storage capacity and error correction degree. The format, red in figure above, has information about error correction and mask pattern.
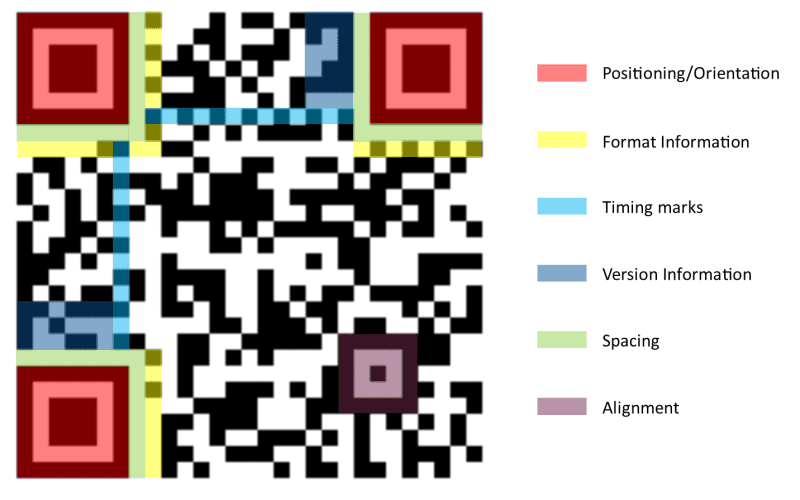
In drawing above, there are highlighted lines in light blue connecting identification squares. Are pixel lines which alternate between white and black. Represent timing, inform coordinates and size of every pixel set. In rest of space are content of codified information.
Masks
Masks change code’s appearance and serve to facilitate reading for scanner. Exist 8 mask patterns.

Information about mask patter is highlighted in green at figure below.
The mask is put in QR code with a logic door XOR. Applying XOR logic again with the same pattern, mask is removed.
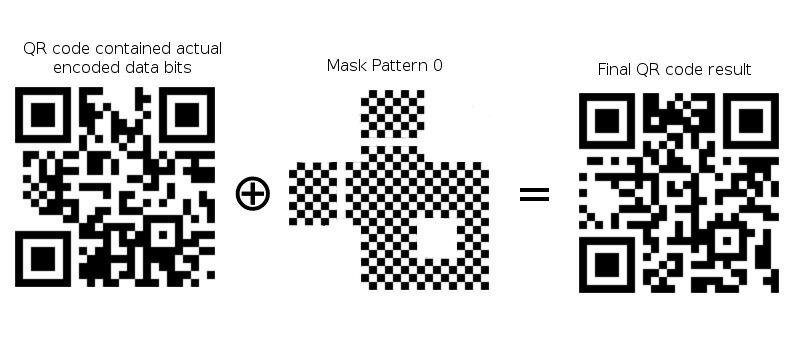
XOR means OR-exclusive and have already been explained in post about combinational circuits.
Error correction
Reed-Solomon error correction algorithm is used. Exist 4 correction levels.
- L (low): 7% of data can be recovered.
- M (medium): 15% of information can be recovered.
- Q (quarter): Allow reading even if 25% of QR was damaged.
- H (high): correction of 30%.
With error correction high enough, it is possible to put drawing inside the code without damage reading.


When higher correction level, lower the capacity to store data.
Reading and creating QR codes
QR code reader application can be downloaded for free in cellphone. Also there are site where it is possible to create it’s own quick response codes for free.



