NASA’s mission Mars 2020, launched yesterday, promises to bring samples from Mars to Earth with Perseverance rover. To find out if existed life.
Source: NASA
Humanity’s most sophisticated rover launched with the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter at 7:50 a.m. EDT (4:50 a.m. PDT) Thursday on a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
The ULA Atlas V’s Centaur upper stage initially placed the Mars 2020 spacecraft into a parking orbit around Earth. The engine fired for a second time and the spacecraft separated from the Centaur as expected. Navigation data indicate the spacecraft is perfectly on course to Mars.
Mars 2020 sent its first signal to ground controllers via NASA’s Deep Space Network at 9:15 a.m. EDT (6:15 a.m. PDT). However, telemetry (more detailed spacecraft data) had not yet been acquired at that point. Around 11:30 a.m. EDT (8:30 a.m. PDT), a signal with telemetry was received from Mars 2020 by NASA ground stations. Data indicate the spacecraft had entered a state known as safe mode, likely because a part of the spacecraft was a little colder than expected while Mars 2020 was in Earth’s shadow. All temperatures are now nominal and the spacecraft is out of Earth’s shadow.
When a spacecraft enters safe mode, all but essential systems are turned off until it receives new commands from mission control. An interplanetary launch is fast-paced and dynamic, so a spacecraft is designed to put itself in safe mode if its onboard computer perceives conditions are not within its preset parameters. Right now, the Mars 2020 mission is completing a full health assessment on the spacecraft and is working to return the spacecraft to a nominal configuration for its journey to Mars.
This spacecraft will arrive at Mars on February 18, 2021.
Perseverance rover of Mars 2020
The Perseverance rover’s astrobiology mission is to seek out signs of past microscopic life on Mars, explore the diverse geology of its landing site, Jezero Crater, and demonstrate key technologies that will help us prepare for future robotic and human exploration.
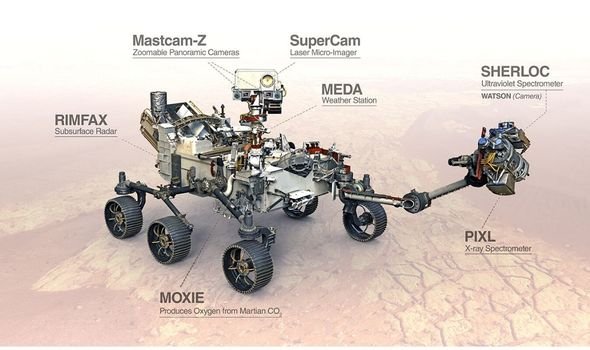
In addition to the instruments shown in the figure above, it possesses a drill to extract samples that will be sent to Earth.
The helicopter Ingenuity

Another mission’s novelty, this helicopter doesn’t carry any scientific instrument. Stays in Perseverance’s belly during the travel to Mars and will fly in Martian skies to test the possibility to use aircraft. Remembering that the atmosphere is much thinner than of Earth.



