Speleothems are rock formations inside caves, the most known are stalactites and stalagmites. These and other formations are shown in this post.
Stalactites, stalagmites and columns
Formations in ceiling of caves pointed down are stalactites and, the ones which are in ground pointed up are stalagmites. Most part of water infiltrating in walls and ceiling in caves come from rains, water with carbon dioxide (CO_{2}) forms carbonic acid (H_{2}CO_{3}). The substance Ca(HCO_{3})_{2} is called sodium bicarbonate. When aqueous solution Ca(HCO_{3})_{2} enters in contact with air, occurs calcite precipitation. Each water drop creates a calcite ring, rings accumulate until form a stalactite.

As for stalagmites, water with CO_{2} drips in ground and forms calcite (CaCO_{3}). Each drop deposites a layer of calcium carbonate. Because of that, most of time stalactites and stalagmites come in pairs. When these two speleothems find each other, form a column. These formation’s growth rate vary between 0.007 e 3 mm/year. Depends on following factors: Water quantity, drip speed, limestone purity and environment’s temperature.
Other materials
In addition to calcite, other materials which form speleothems are aragonite and gypsum. Aragonite has the same chemical formula of calcite CaCO_{3}. Difference is in crystalline structure.

Other material used in speleothems formation is gypsum, whose formula is CaSO_{4}\cdot 2H_{2}O. Water evaporation produces CaSO_{4}\cdot 0,5H_{2}O.
Some other speleothems
In addition to stalactites and stalagmites, exist many other formations inside the caves.
Curtains

In an inclined ceiling or wall cave, drop which appears ceiling’s surface instead of fall until evaporates, it’s because of Coandă effect. Leaving a trail of calcite, the next drops follow the same path. Many layers form curtain which sometimes reminds bacon. When water drops contain iron oxide, clay or other organic material, curtains produce yellow, brown or orange colors. Concentration variations create layers with different shades in same curtain.
Cauliflower or popcorn
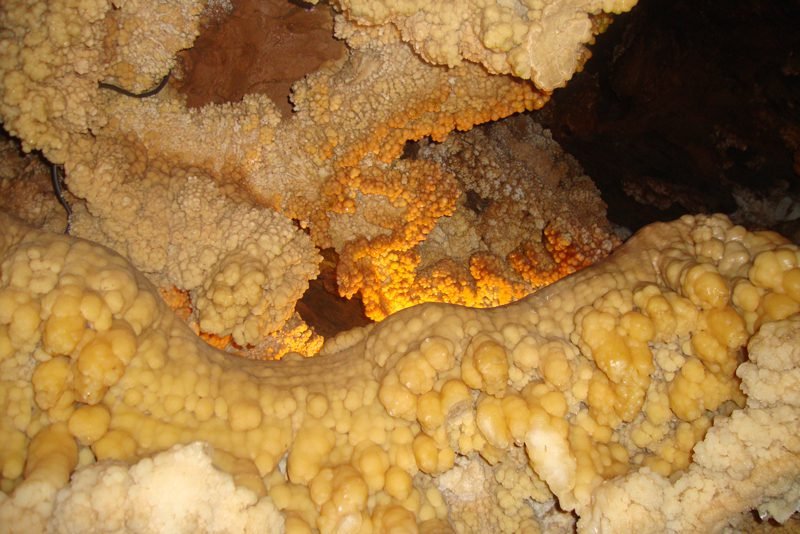
When drop falls in an irregular surface, carbonic acid is splashed with shock in roughened surface. Can appear in floors or walls.
Helictites
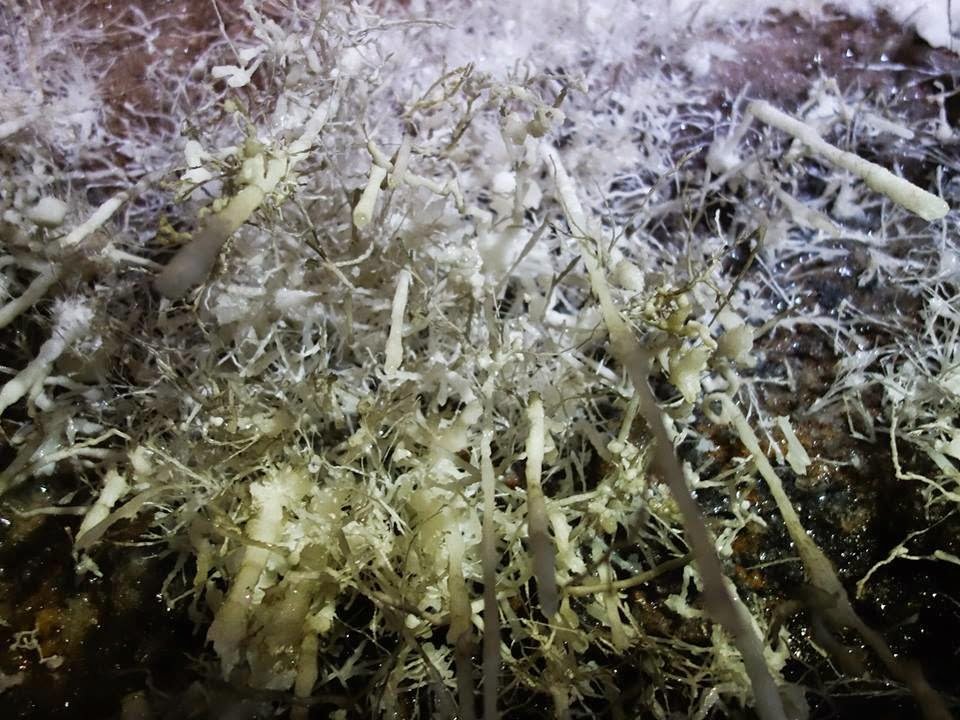

This speleothem appears like a small stalactite, when grows, assumes an irregular shape. There’s still no explanation for helictites. Some hypothesis suggest wind action, tube’s interruption and water impurity.
Cave flowers
Instead of growing perpendicularly to surface, this speleothem grows sideways forming curves around an axis. Usually are made of gypsum and exist in many different shapes. Growth direction is caused by gypsum precipitation. Curvatures are caused by variation flux of saturated water.
Boxwork

It’s a rare formation, caused by erosion or weathering of limestone. Water fills cracks in ceiling or wall, depositing thin calcite layers.
Flat formations

In some caves, calcite plates can be seen on water. Calcite is deposited on water surface when there is liberation of carbon dioxide and steam. Are very fragile and with time they sink, forming a layer in deep. Can hold in walls, forming platforms or gradually form “tables” with layers below.
Featured image
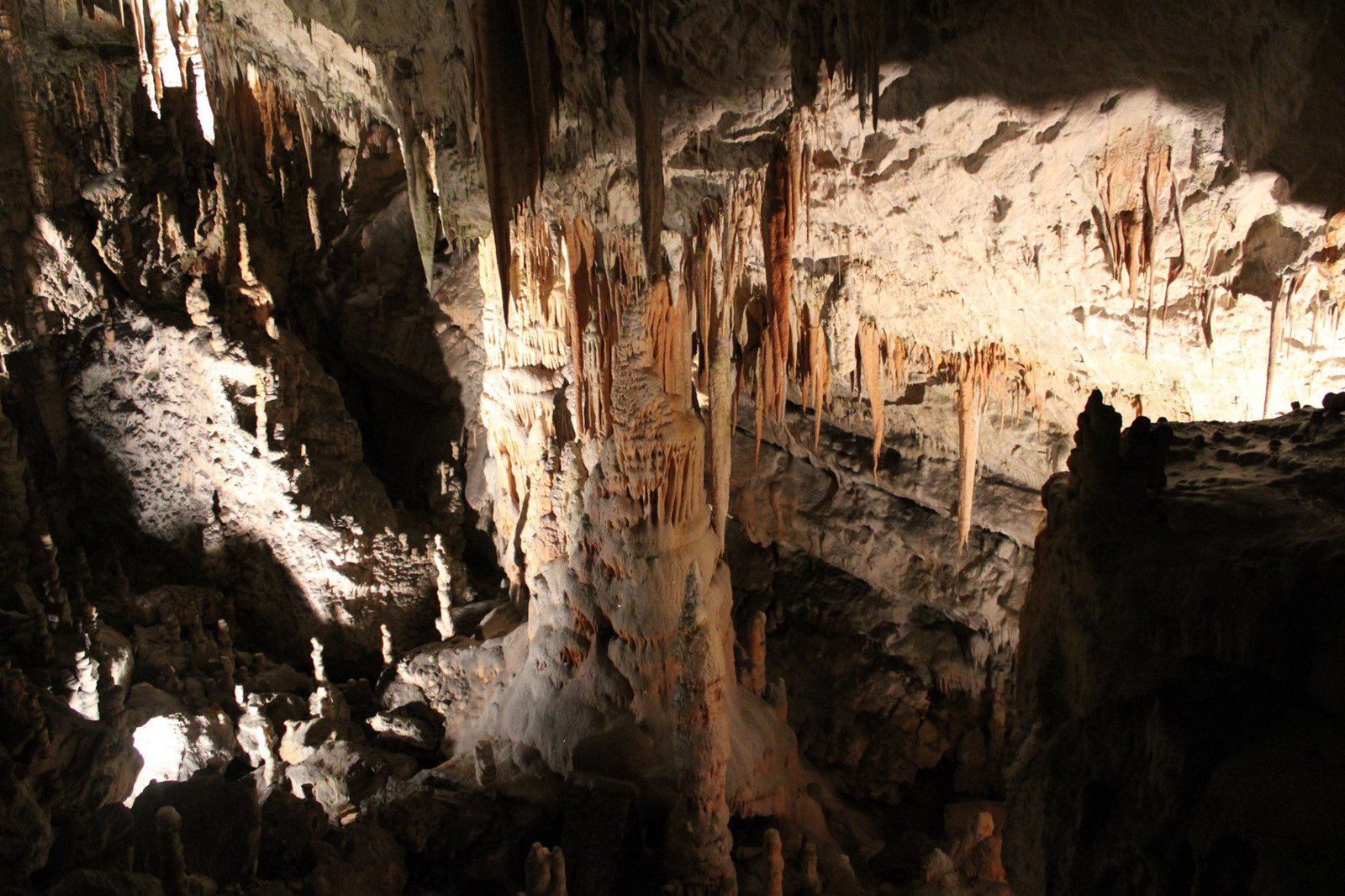

This post’s featured image, which appears in home page, is from Postojna cave, Slovenia. I wrote two post about it.
Postojna cave (Part 1)Click here
Postojna cave (Part 2)Click here


