UPS (the abbreviation of Uninterruptable Power Source) is also called no-break. The operation and types are today’s subject.
What is the finality and how it works?
When the power through the grid is down, UPS supplies the devices with a battery or battery bank. That’s why it’s called no-break. This equipment prevents you to lose the work on the computer due to blackouts. Giving time to save and shut down the PC properly, before discharge the battery.
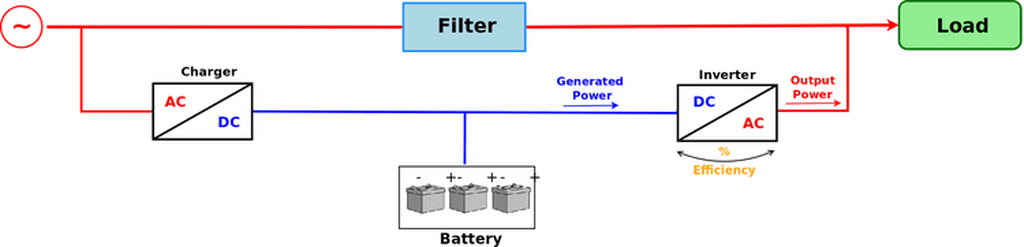
When there’s electric energy from grid, the battery is charged with a rectifier, converts alternate current (AC) in direct current (DC). An inverter does the reverse conversion, DC in AC.
I already wrote a post about inverter’s operation. Access in link below.
How the inverter works?Click here
The filter serves to protect the load against grid’s fluctuations (abrupt variations of voltage and/or frequency) and noises. UPS must have a transfer or bypass switch to use battery only when necessary.
Exist no-breaks of many sizes and can supply a great variety of equipment, not only computers.

The no-break’s power is measured in VA, the value of apparent power. The time it can provide energy depends on UPS power and devices’ consumption.
Difference between UPS and stabilizer
Although some look like a stabilizer for desktop PC, aren’t the same thing. The main difference is that no-break has a battery. As the name says, the stabilizer keeps plug voltage stable to protect sensitive PC’s components and it’s peripherals.
UPS topologies
Standby
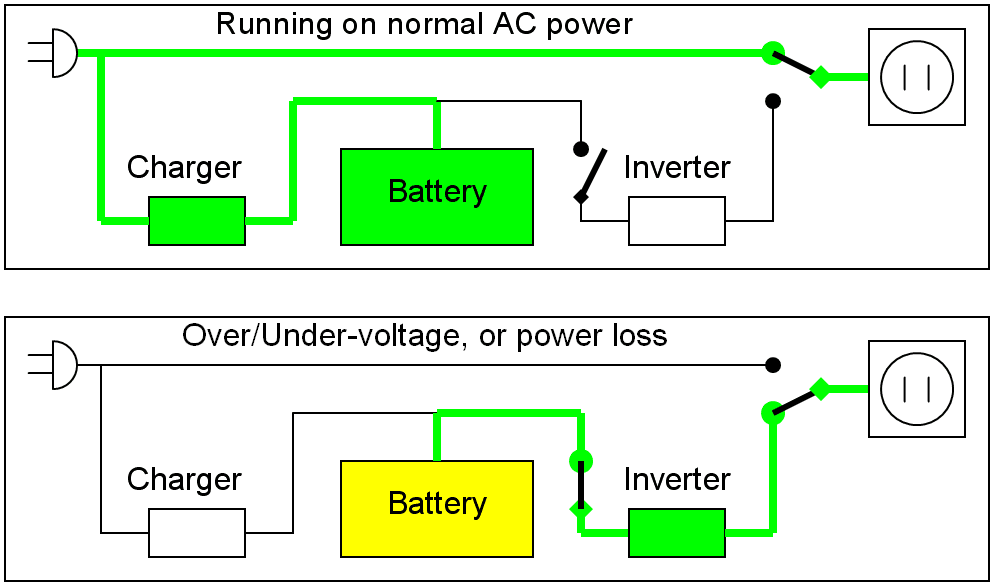
It is the simplest and cheapest type. When the grid’s energy fall to a determined level, the battery supply system is used to avoid device’s sudden shutdown.
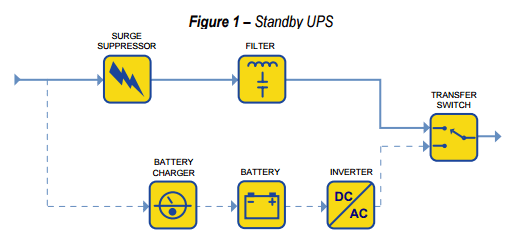
This type is recommended to home and office machines, like PCs. Isn’t indicated for hospital equipment and more sensitive ones. Not all of this topology have protection against fluctuations from the power grid.
Line-interactive
This topology has an automatic voltage regulator (AVR), control voltage variations from the grid. Without AVR, would have to use battery without necessity.
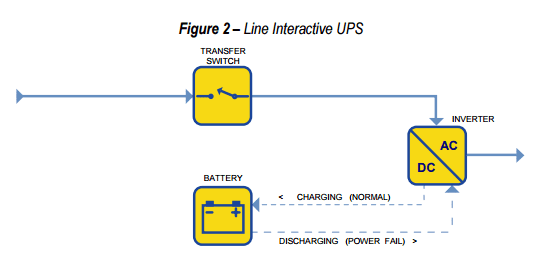
While there is grid energy, the battery is charged. And it’s used when there is a power shortage, activating inverter in reverse. As the inverter/rectifier is always online, the response time is shorter than standby. It’s used in servers of small companies, industrial control systems, network equipment, home theater, and other more demanding but cheaper applications.
Double conversion or online
The two topologies shown before are offline. In double conversion, the grid’s signal is always rectified and then converted to alternate by an inverter. Therefore, there isn’t a change interval for battery mode.
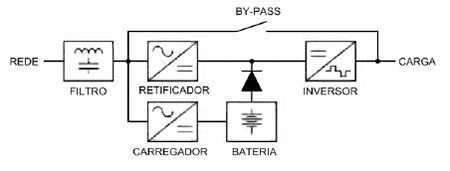
Produces the best waveform in output, independent of the grid’s conditions. However, are more and the battery lasts less time. Supply sensitive equipment which need high-quality energy, for example, hospital machines.
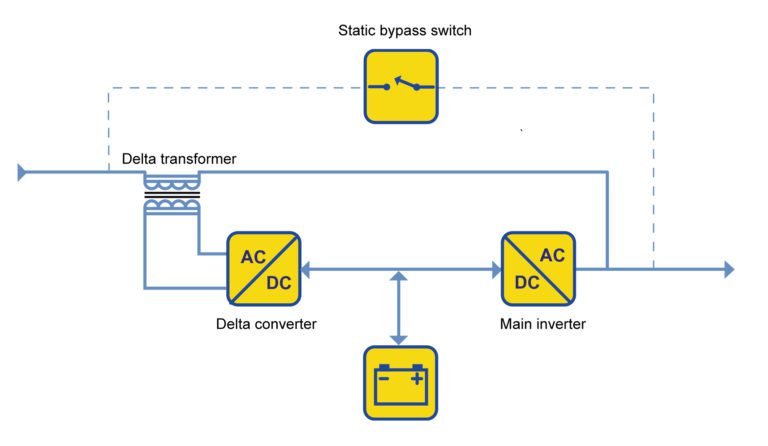
Delta conversion
It’s more efficient than double conversion. Has a delta transformer that provides additional power to load.
Waveforms
The no-breaks can provide three waveforms in output.
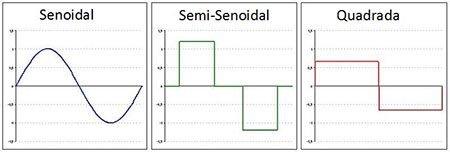
The simplest and cheapest transmit squarewave. The best and most expensive generate the sinusoidal wave. While semi-sinusoidal is for intermediary applications.


