In addition to parallel and series, impedances also can make star and delta connections. Also are shown the transformations.
Star and delta connections
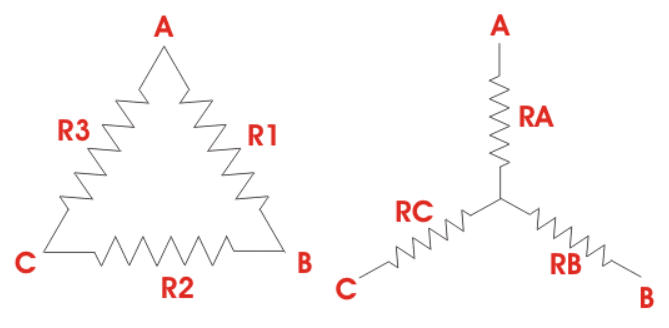
Some sources label delta connection as pi and star as T.
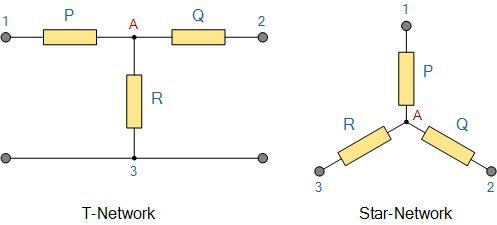
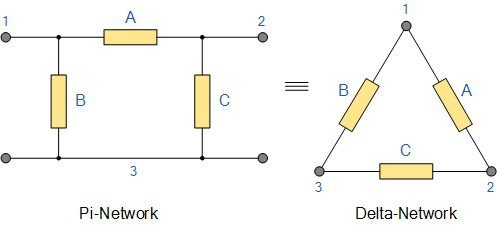
Star-delta transformation (Y-Δ)
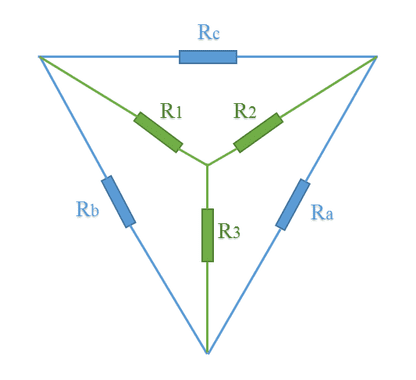
Equations to transform a star configuration to delta.
Ra=\frac{R_{1}R_{2}+R_{1}R_{3}+R_{2}R_{3}}{R_{1}}
Rb=\frac{R_{1}R_{2}+R_{1}R_{3}+R_{2}R_{3}}{R_{2}}
Rc=\frac{R_{1}R_{2}+R_{1}R_{3}+R_{2}R_{3}}{R_{3}}
Delta-star transformation (Δ-Y)
Equations for (Δ-Y) transformation.
R_{1}=\frac{RbRc}{Ra+Rb+Rc}
R_{2}=\frac{RaRc}{Ra+Rb+Rc}
R_{3}=\frac{RaRb}{Ra+Rb+Rc}
If all resistors are equal, the equations become much simpler. Considering R_{Y} as resistor value in star and R_{\Delta } of resistor in delta.
R_{Y}=\frac{R_{\Delta }}{3}
R_{\Delta }=3\cdot R_{Y}
Transformation with capacitors and coils
What if instead of resistors, we have capacitors and coil?
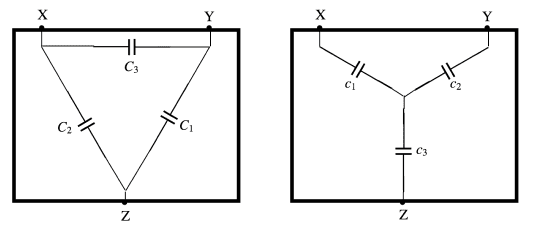
Demonstrating the equation of (Δ-Y) transformation for capacitors.
\frac{1}{c_{1}}=\frac{\frac{1}{C_{2}C_{3}}}{\frac{1}{C_{1}}+\frac{1}{C_{2}}+\frac{1}{C_{3}}}
c_{1}=\frac{C_{2}C_{3}+C_{3}C_{1}+C_{1}C_{2}}{C_{1}}
c_{2}=\frac{C_{2}C_{3}+C_{3}C_{1}+C_{1}C_{2}}{C_{2}}
c_{3}=\frac{C_{2}C_{3}+C_{3}C_{1}+C_{1}C_{2}}{C_{3}}
Equations for inverse transformation (Y-Δ).
\frac{1}{C_{1}}=\frac{\frac{1}{c_{1}c_{2}}+\frac{1}{c_{1}c_{3}}+\frac{1}{c_{2}c_{3}}}{\frac{1}{c_{1}}}
C_{1}=\frac{c_{2}c_{3}}{c_{1}+c_{2}+c_{3}}
C_{2}=\frac{c_{1}c_{3}}{c_{1}+c_{2}+c_{3}}
C_{3}=\frac{c_{1}c_{2}}{c_{1}+c_{2}+c_{3}}
And for inductors, the calculations are similar to resistors.
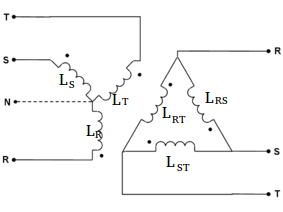
Equivalent values from Y to Δ.
L_{RS}=\frac{L_{R}L_{S}+L_{S}L_{T}+L_{R}L_{T}}{L_{T}}
L_{RT}=\frac{L_{R}L_{S}+L_{S}L_{T}+L_{R}L_{T}}{L_{S}}
L_{ST}=\frac{L_{R}L_{S}+L_{S}L_{T}+L_{R}L_{T}}{L_{R}}
Equivalent values from Δ to Y.
L_{R}=\frac{L_{RS}L_{RT}}{L_{RS}+L_{RT}+L_{ST}}
L_{S}=\frac{L_{RS}L_{ST}}{L_{RS}+L_{RT}+L_{ST}}
L_{T}=\frac{L_{ST}L_{RT}}{L_{RS}+L_{RT}+L_{ST}}
And for impedances.
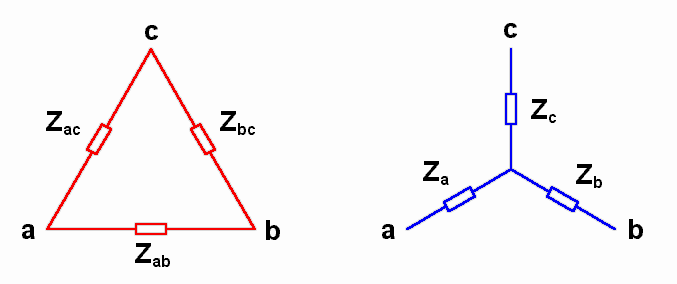
Conversion from Y to Δ.
Z_{ac}=\frac{Z_{a}Z_{c}+Z_{a}Z_{b}+Z_{b}Z_{c}}{Z_{b}}
Z_{ab}=\frac{Z_{a}Z_{c}+Z_{a}Z_{b}+Z_{b}Z_{c}}{Z_{c}}
Z_{bc}=\frac{Z_{a}Z_{c}+Z_{a}Z_{b}+Z_{b}Z_{c}}{Z_{a}}
Conversion from Δ to Y.
Z_{a}=\frac{Z_{ab}Z_{ac}}{Z_{ab}+Z_{ac}+Z_{bc}}
Z_{b}=\frac{Z_{ab}Z_{bc}}{Z_{ab}+Z_{ac}+Z_{bc}}
Z_{c}=\frac{Z_{ac}Z_{bc}}{Z_{ab}+Z_{ac}+Z_{bc}}
3 problem examples
Let’s find the value of I current in this circuit.
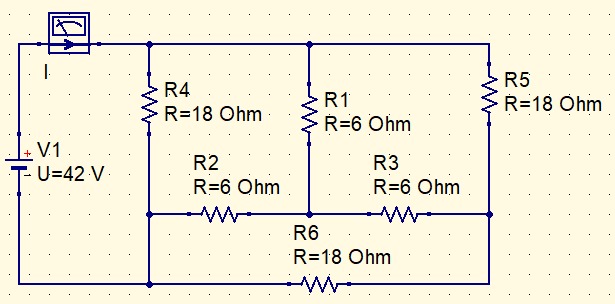
Converting internal star in delta.
R_{\Delta }=3\cdot R_{Y}
R_{\Delta }=3\cdot 6=18 \Omega
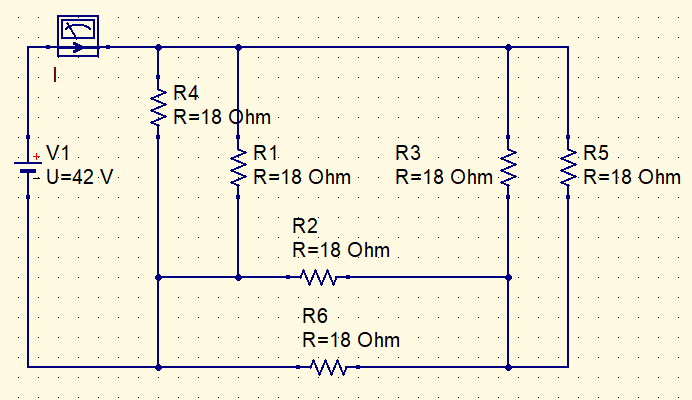
3 resistor pairs are in parallel. Just simplify the circuit to find I current.
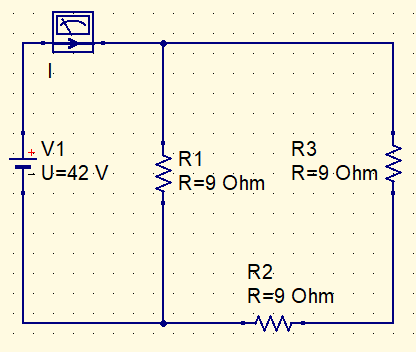
Rt=\frac{9\cdot 18}{9+18}=6\Omega
I=\frac{42}{6}=8A
How to calculate I current in this circuit?
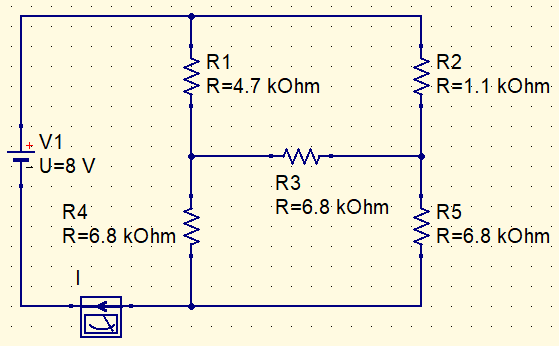
Replacing R1, R2 and R3 with (Δ-Y) tranformation.
Ra=\frac{4,7k\cdot 1,1k}{4,7k+1,1k+6,8k}=\frac{5,17k}{12,6}=0,41k\Omega
Rb=\frac{4,7k\cdot 6,8k}{4,7k+1,1k+6,8k}=\frac{31,96k}{12,6}=2,53k\Omega
Rc=\frac{1,1k\cdot 6,8k}{4,7k+1,1k+6,8k}=\frac{7,48k}{12,6}=0,59k\Omega
With simplified circuit, becomes easier to calculate current.

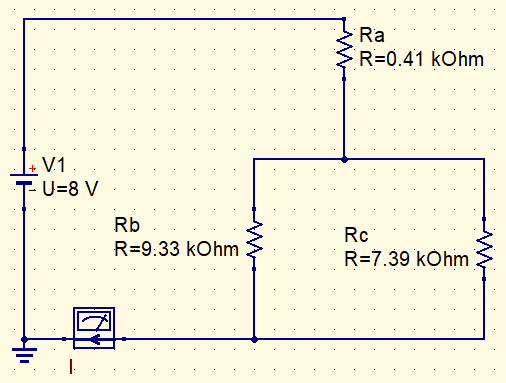
Rt=\frac{9,33k\cdot 7,39k}{16,72k}=4,12k\Omega
I=\frac{8}{0,41k+4,12k}=1,76mA
How to find total resistance of this resistor association?
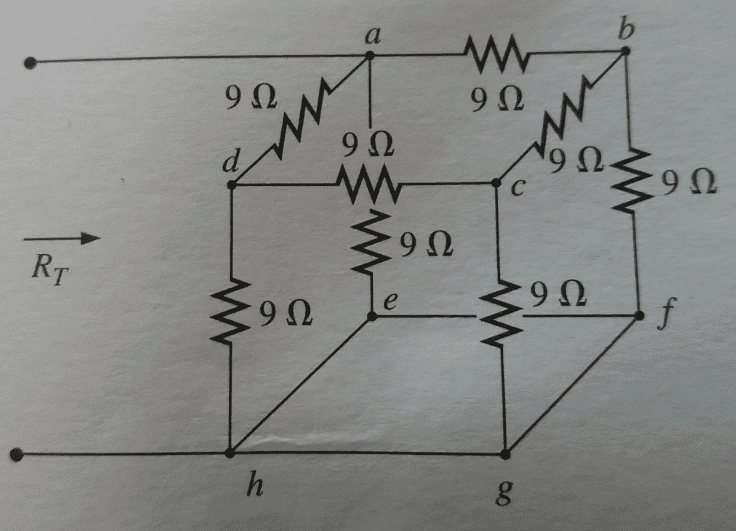
Putting this cube in a shape that allows to visualize a group of resistors for conversion.
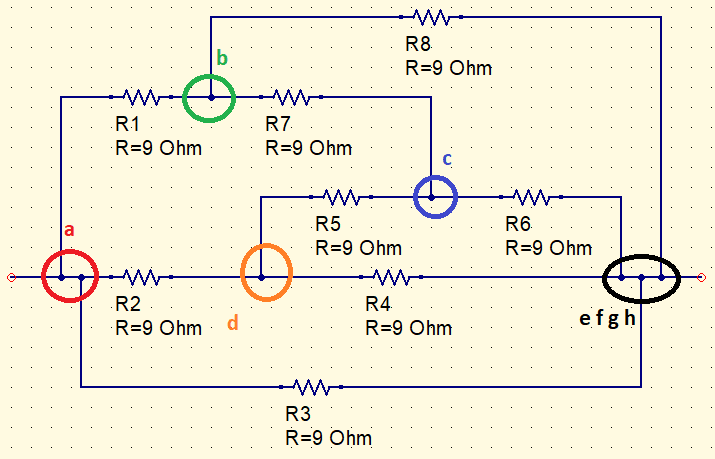
R_{Y}=\frac{R_{\Delta }}{3}=\frac{9}{3}=3\Omega

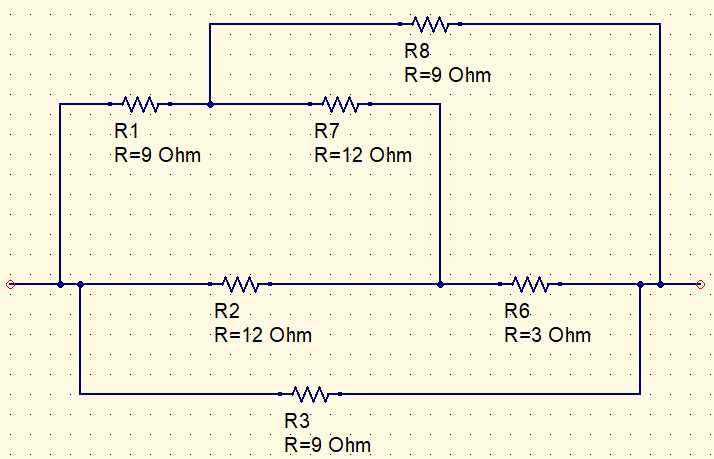
Converting delta on the left in star.
R_{a}=R_{b}=\frac{R1\cdot R2}{R1+R2+R7}=\frac{9\cdot 12}{33}=3,27\Omega
R_{c}=\frac{12\cdot 12}{9+12+12}=4,36\Omega
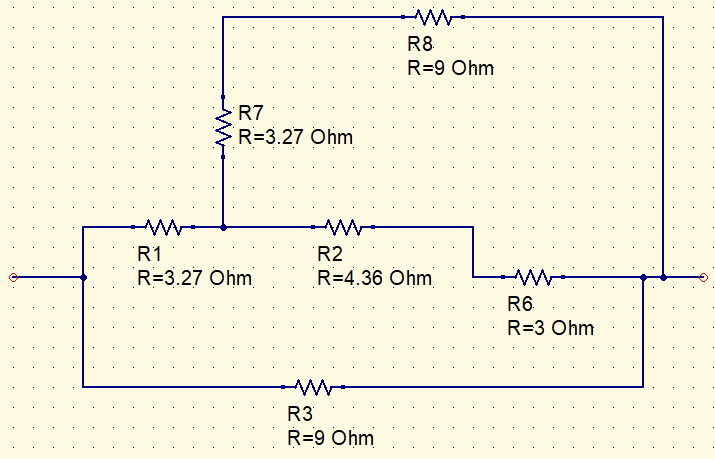
R7+R8=12,27\Omega
R2+R6=7,36\Omega
\frac{12,27\cdot 7,36}{12,27+7,36}=4,6\Omega
3,27+4,6=7,87\Omega
Finally, the total resistance is:
Rt=\frac{9\cdot 7,87}{9+7,87}=4,19\Omega


