This post’s subject is cloud computing, a service that allows using computational resources without purchase necessary equipment and programs.
How it works?
Cloud computing allows outsourcing storage and other computational services. Through the internet, it’s possible to access these resources without the necessity to save files and install programs on the client’s computer. When it’s said that data are stored in the cloud, actually means that is stored in a data center.
The data center belongs to a company that provides this service, known as CSP (Cloud Service Provider). This service is possible thanks to increasing internet speed and to virtualization, a technology that allows the simulation of entire computers e IT (Information Technology) services without the acquisition of required hardware. With virtualization, a single PC can run both Windows and Linux. An operational system simulator is popularly known as a virtual machine.
Vantages and disadvantages of cloud computing
The vantages of using cloud computing are:
- Cost reduction: With the outsourcing of services, there isn’t a necessity to purchase hardware, install or configure programs.
- Flexibility: It’s possible to access files and services in the clouds anywhere, as long as you have internet access.
- Performance: Data centers that provide cloud service are updated when it’s necessary, to keep performance.
While the disadvantages:
- Risks to privacy and security, sensitive information can be leaked.
- Delay and difficulty to change server.
Types of cloud
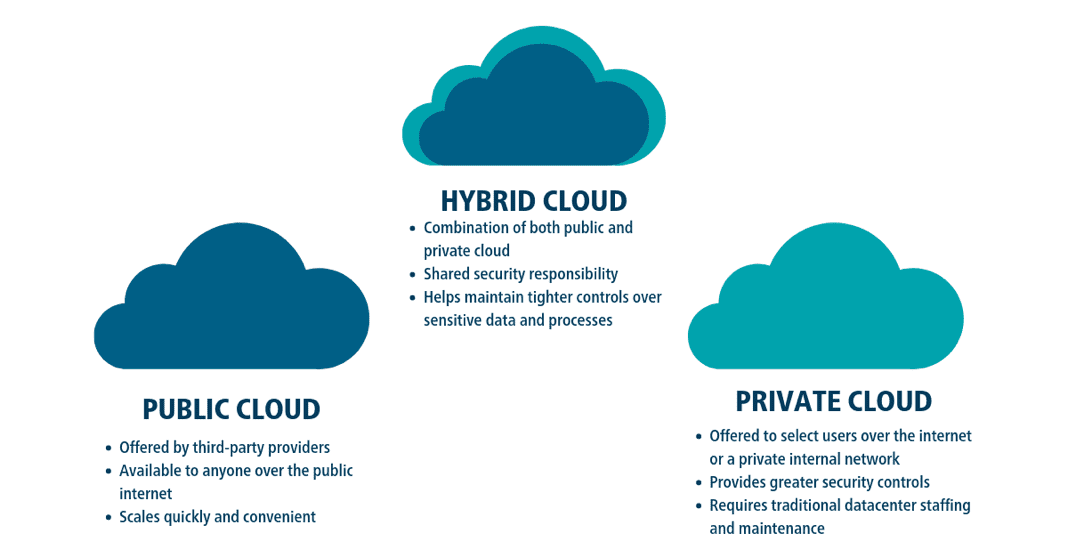
In addition to information from the figure above:
- Public cloud: Has standardized architecture. But it’s harder to manage and evaluate access control. Also has a higher risk to privacy and security.
- Private cloud: Generally used exclusively by a single corporation or organization, located in a local data center of this corporation. Requires high investment cost.
- Hybrid cloud: Has a link that connects public and private clouds. Very used in e-commerce.
Models and examples of cloud computing
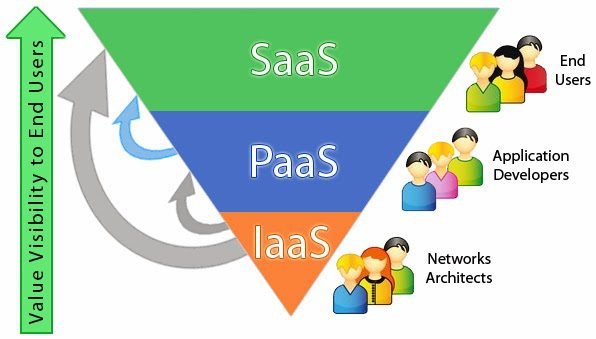
Software as a service (SaaS)
Allows to use apps online without install on the computer, needs only to make an account. For example, Office 365, where you can use Microsoft Word, Excel, PowerPoint, etc., without installing these programs on your computer.

E-mail services and GoogleDocs as also SaaS examples.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Provides a development environment and app implementation on cloud, the user does not need to manage infrastructure and receive the necessary resources from the provider. A PaaS is built with containers, which are packaged microservices with configurations. Containers are managed by open source software called Kubernetes. Some examples are Microsoft Azure and Google App Engine.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Are offered virtual servers, network connections, virtual machines, storage, and operational systems. Dismissing the necessity to purchase its own equipment. However, the client does not control the infrastructure. The tariff is based on service and depends on the number of virtual servers, the quantity of trafficked data, storage, and other items. Some examples are Amazon Web Services and Rackspace.


