In this third part, are shown the operation principle, advantages and disadvantages, and the applications of fiber laser.
Links to access the previous parts.
Fiber laser structure
The medium gain is made of optical fiber doped with erbium (Er), ytterbium (Yb), neodymium (Nd), thulium (Tm), holmium (Ho) or praseodymium (Pr). All these elements are rare earths. These elements absorbs most of photons (light particles) that comes from the source and re-emits to make the stimulated emission, producing a high quality and power beam. Each doped fiber with a rare earth element produce a different wavelength.
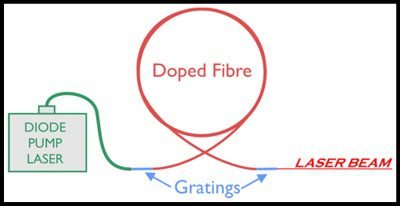
Instead of mirrors, are used Bragg gratings, structures composed of stripes on fiber’s core that reflect light with a determined wavelength. The Bragg gratings have refraction index different from the rest of core fiber.
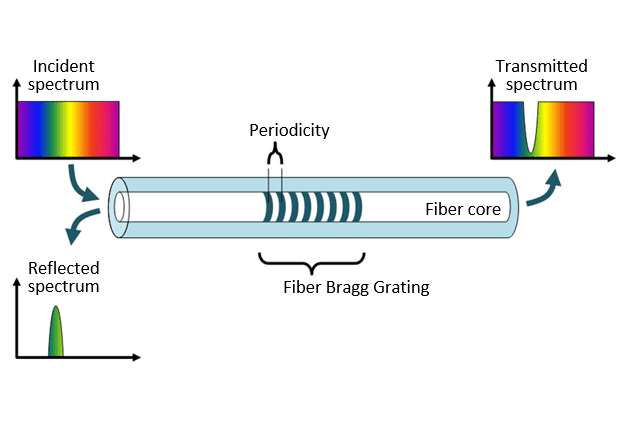
The distance between Bragg gratings or periodicity, determine the wavelength that will be reflected.
Advantages and disadvantages of fiber laser
The advantages of fiber laser are:
- Stability: to put a laser beam of other type in an optical fiber, it is necessary fine tune of beam and mirrors. In this type, the stimulated emission is made inside the fiber’s core, therefore, doesn’t need complex and sensitive optical equipment. It can resist to vibrations and motions.
- High quality: it means that the beam is very narrow and can be focused in a very small area, indicating little divergence on propagation.
- Efficiency: fiber laser has an energetic efficiency between 70 and 80%. Almost 100% of diode laser energy is converted to produce the beam inside the medium gain. Therefore, doesn’t need an active cooling system.
While the disadvantages:
- The doped fiber is expensive.
- The fiber is fragile.
- Fiber laser cutting machines don’t serve to cut non-metals. In this application, are more used carbon dioxide (CO_{2}) lasers.
- The fiber size limits laser power.
Some applications
- The capacity to focus the beam in a very small area is a useful feature to cut and drill metal sheet.
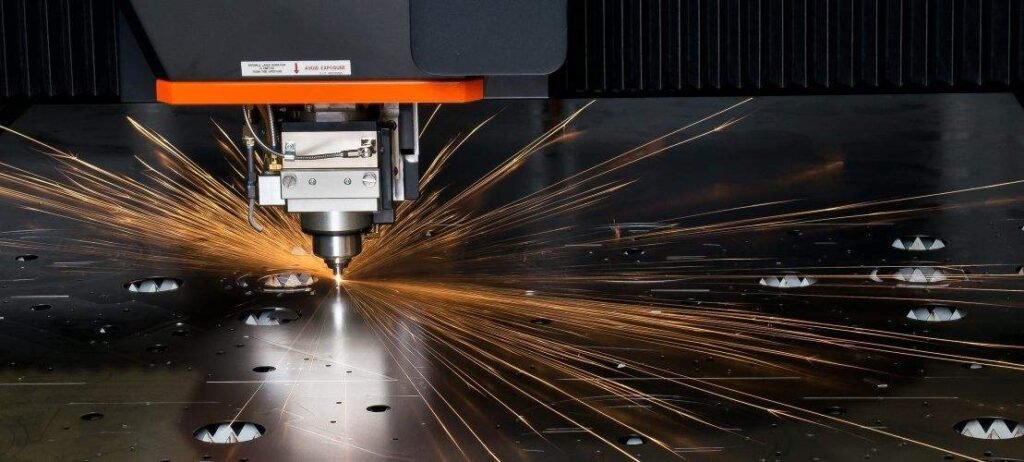

- Are used in medicine as shown in the second post about rare earths.
- This type of laser is used in LIDAR, it’s like a radar, but uses laser pulses instead of radio waves to measure distances and detect objects.