In this post, it’s shown the methods of detecting exoplanets, which are planets outside the Solar System, they orbit other stars or wandering through space.
Direct imaging
Consists in observe directly the celestial body directly through a telescope. However, it’s very hard to find planets several light-years away with this technique. Few exoplanets have been discovered with direct imaging. The greatest difficulty is that the light reflected by the planet and heat radiation are overshadowed by the star’s brightness. One of the ways to block a star’s light is to equip the telescope with a coronograph. This has already been quoted in the post about coronal mass ejection.
What is coronal mass ejection?Click here

Gravitational lens
The gravitational lens uses the General Relativity principle, light bends and changes direction when pass close to a massive object.
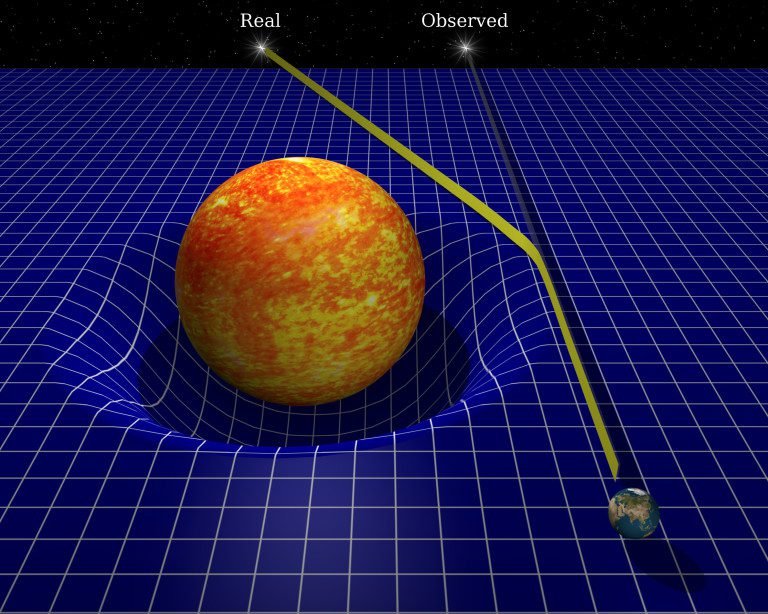
To use this method, a source star is used to provide a backlight, while the exoplanet’s star serves as a lens to bend the light and produce two images from the source star.
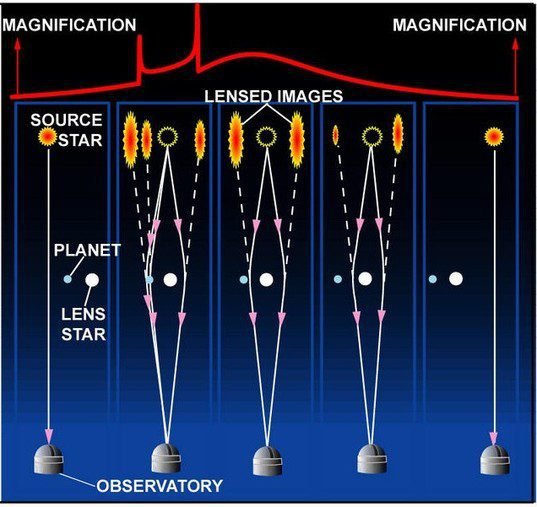
Star’s brightness variation
This is the most used method to find exoplanets. The majority of planets outside the Solar System were discovered by observing the variation of brightness on target star.
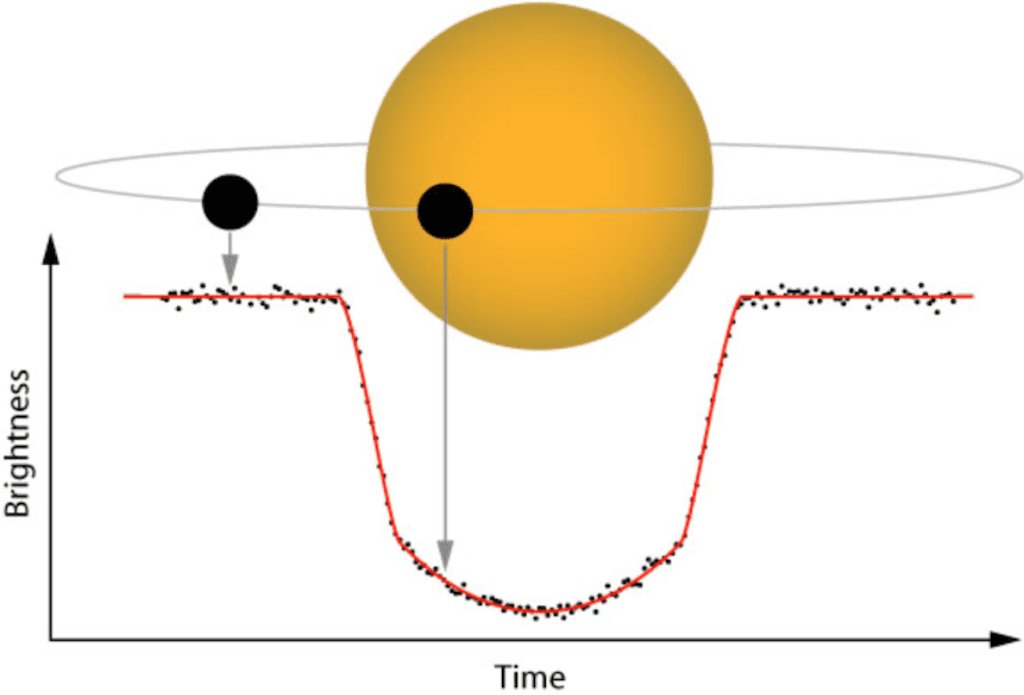
With this method, can also discover the planet size and its translation speed, which is related to the distance from the star. The disadvantage of this method is that the exoplanet can take too long to pass in front of the star.
Radial speed variation
The star exerts a gravitational force on the planet and vice versa. Consequently, both spin around a common center of mass for both celestial bodies.
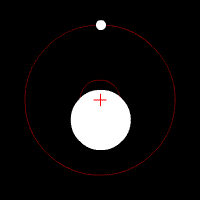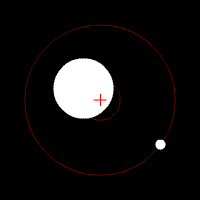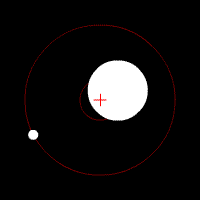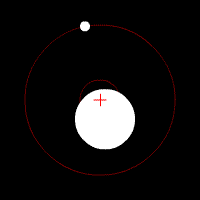
This movement causes a Doppler effect, emitted light by the star causes a wavelength variation in relation to the telescope.
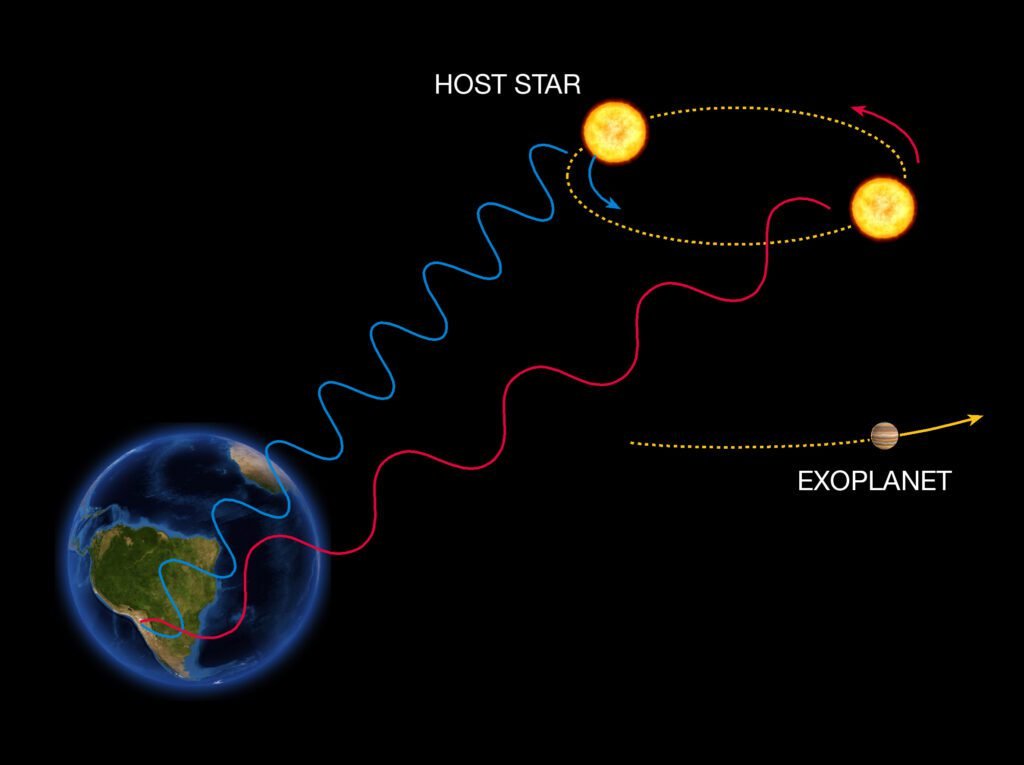
Measuring the variation wavelength can measure sa tar’s oscillation speed. Therefore, can calculate the mass and speed of the planet. This method is useful only to find massive exoplanets around small stars.
Astrometry
This method consists in detect the motion of a star by measuring its distance in relation to other stars that are fixed in relation to observer.
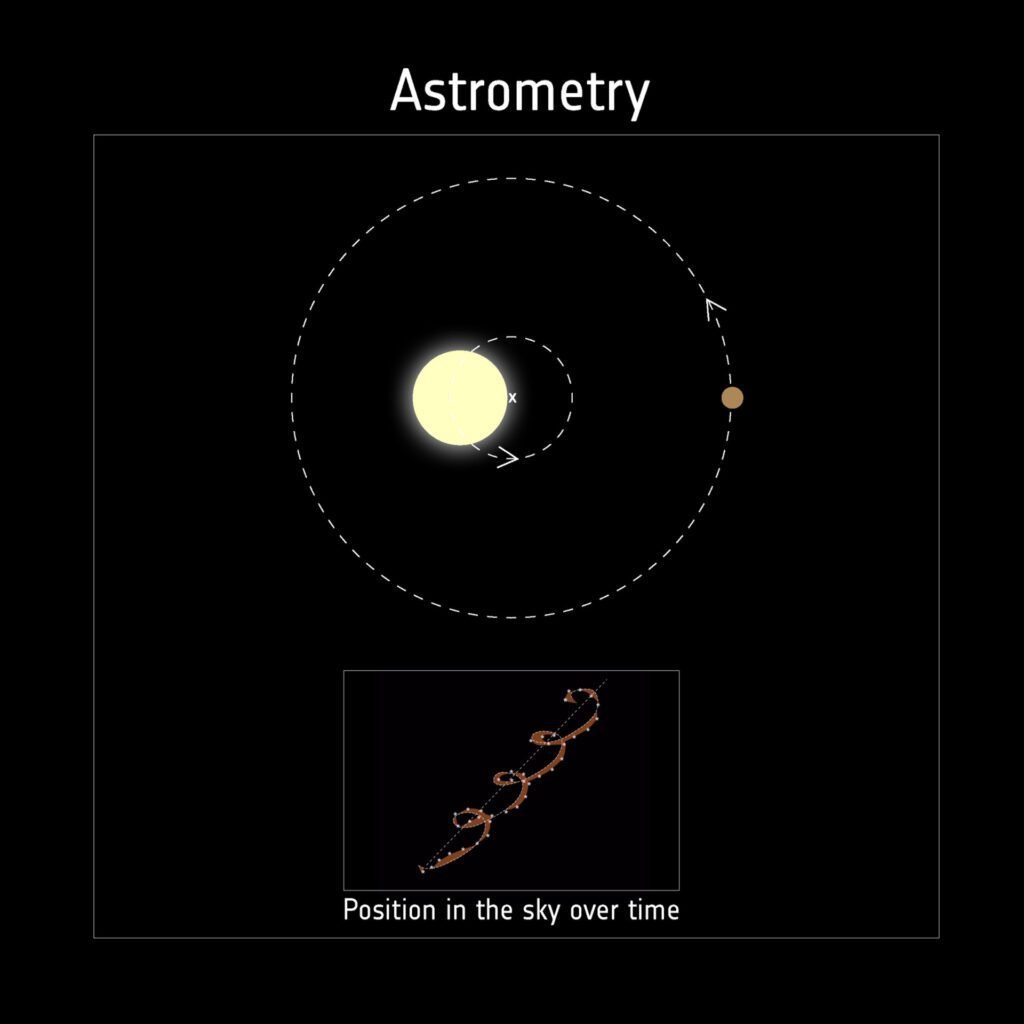
Many images of the region in space where the target star is located are taken to compare the distances with reference stars. This method is very difficult to use and requires optical instruments extremely precise. Very few exoplanets were discovered with this technique.



