Wentian is a space lab that will be coupled to Tianhe, the main module of the Chinese space station. Was launched by Long March 5B rocket.
News with information about the Tianhe module.
Source: Space.com
Wentian was sent on its way to orbit atop a Long March 5B heavy-lift rocket that blasted off at 2:25 a.m. EDT (0625 GMT or 2:25 p.m Beijing time) on July 24 from the Wenchang spaceport on the southern island of Hainan. The 58.7-foot-long (17.9 meters) module will soon match the orbit of Tianhe, China’s first space station module, which launched in April 2021. Wentian is expected to rendezvous and dock with a port attached to Tianhe later on Sunday.
Wentian, which literally means “quest for the heavens,” is the second of three modules planned for launch by China. A third, named Mengtian, is scheduled to launch in October and will complete the T-shaped Tiangong space station. Including a Shenzhou crew spacecraft and Tianzhou cargo vessel docked at the station, the completed Tiangong will be around 20% as massive as the International Space Station (ISS), which has a mass of about 460 tons.
Three astronauts of the Shenzhou 14 mission are currently aboard Tianhe awaiting the arrival of the new module. The trio will later host a first live science lecture from Wentian in the near future, according to Chinese state media, following tests.
Wentian’s main role is hosting a series of experiment cabinets that allow astronauts to conduct a wide range of science experiments in orbit; it also carries solar arrays and a new airlock for spacewalks. In addition, it features extra astronaut sleeping quarters to allow China to conduct crew handovers during which six crew members temporarily stay aboard Tiangong; the first such handover is expected to occur before the current crew’s departure in December.
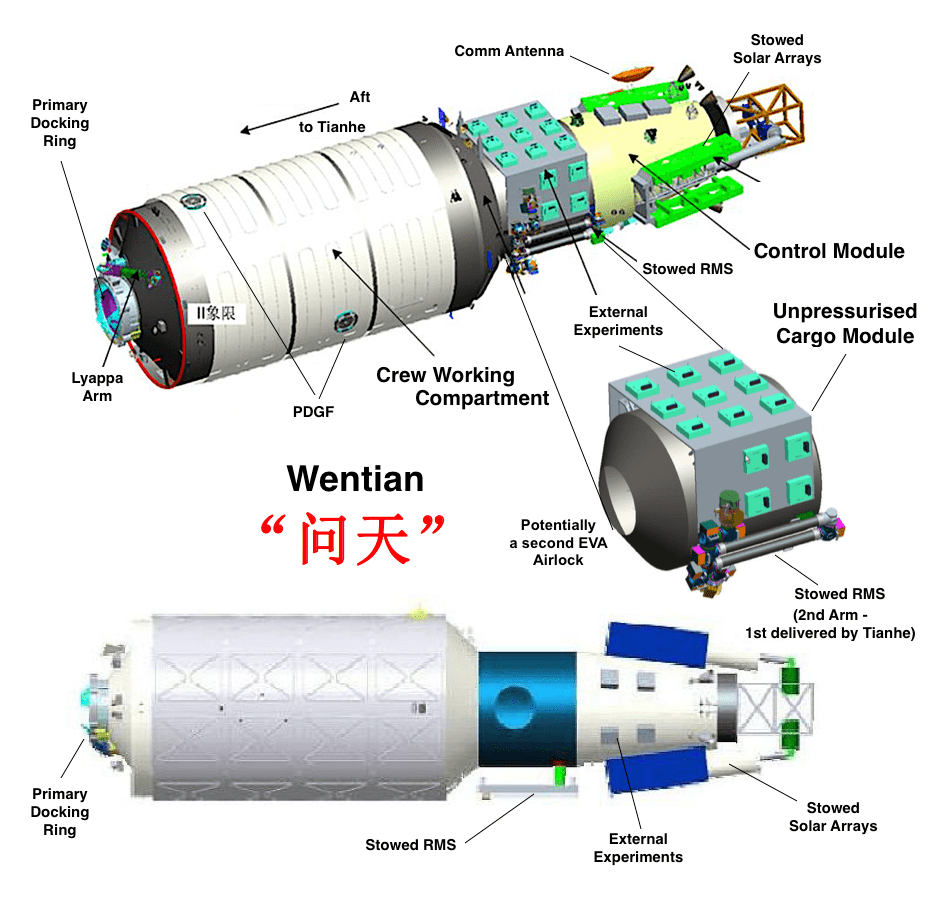
Although Wentian will begin its stay at Tianhe’s forward docking port, the main module’s 33-foot-long (10 m) robotic arm will be used to reposition Wentian to a side port at some time in the coming months. Earlier this year, China tested the necessary maneuvers using Tianzhou 3, a cargo spacecraft that delivered supplies to the space station to support an earlier crew mission. The spacecraft was released days ago to make way for the arrival of Wentian.
Wentian also carries its own 16.4-foot-long (5 meters) robotic arm, which will be able to operate independently or connect with its larger Tianhe sibling arm.
China began its space station project way back in 1992, approving a plan to develop the capability to launch astronauts into space, test life support aboard small space labs, and build new, large rockets capable of launching modules like the roughly 48,500 pounds (22,000 kilograms) Tianhe and Wentian modules.
The country plans to keep the Tiangong space station permanently crewed for at least a decade, with each crew of three astronauts spending six months on board. China has also said it will allow foreign astronauts and even space tourists to visit the orbital outpost in the future, while also hosting international experiments, the first ones have already been selected.
The space station will also support a powerful survey space telescope named Xuntian that China plans to launch around 2024. The Hubble-class observatory will operate in a similar orbit to that of Tiangong, meaning it will be able to dock at the station for refueling, upgrades, and repairs.

Experiments on Wentian
Source: CGTN
The cabin Wentian is mainly for studies on space life sciences. It is equipped with scientific cabinets that can support experiments on life and ecology, biotechnology, as well as comparative studies of biological growth mechanisms under varying gravity conditions.
The experiment cabinets can be used to study the growth, development, heredity, and aging of plants, animals, and microorganisms in space, as well as the research on closed ecosystems. Multi-level biological experiments on molecules, cells, tissues, and organs can be conducted.

