This post subject is phased array antennas. They are many arranged radiators to behave like a single antenna.
Operation principle
The phased array antennas behave like a single antenna which can change the propagation direction of an electromagnetic wave without executing a mechanical movement, using the principle of wave interference.
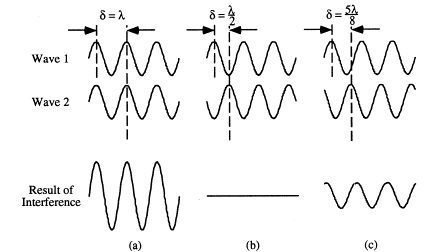
Constructive and destructive interferences
When two or more waves meet each other at a point, occurs an interference. The interference will be totally constructive (on the right) if waves have the same phase and the resulting wave will have a higher amplitude than the individual ones that met each other. If the phase difference is 180º, interference is totally destructive (on the left) and waves cancel each other.

What If the phase difference is between 0 and 180º (or π)? When closer to 0, more constructive will be and when closer to 180º, more destructive will be the interference.
Phased array antennas
If all antennas transmit at same phase, the resulting electromagnetic wave will spread in the perpendicular direction to antennas’ alignment.
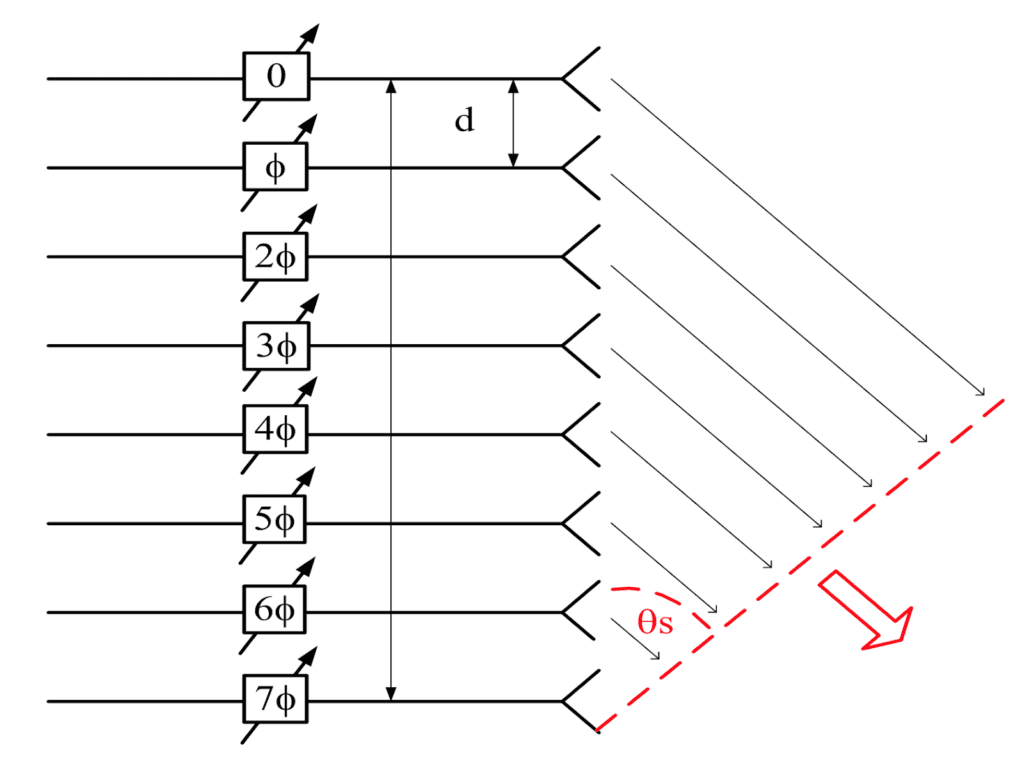
The formula to calculate phase variation (\Delta\phi) between antennas.
\Delta\phi=\frac{360^{\circ}d\cdot sen(\theta_{S})}{\lambda}
Where \lambda is transmitted wave’s wavelength.
Types of phased array antennas
- Linear arrangement.
- Planar arrangement.

- Frequency sweep array: each radiator transmits in a different frequency to change propagation direction. It’s simpler because it doesn’t have phase shifters, but, for using many frequencies, it’s more subject to interference and has bandwidth limitations.
- PESA (Passive Electronically Steered Array): A single transceiver (transmitter and receiver) is used for all antennas.
- AESA (Active Electronically Steered Array): each radiator has a transceiver and a receiver.
- HBF (Hybrid Beam Forming): the combination of PESA and AESA, the array is divided into subarrays and each one of the subarrays has a transceiver for an antenna subarray.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages are:
- Allow a very fast beam’s direction change.
- The replacement of mechanical parts for electronics makes the system lighter.
- High directivity, which reduces interference.
- Allow many directions.
The disadvantages:
- Sweep is limited to 120º on both axes.
- Still expensive.
- High complexity.
Some applications
- 5G wireless communication systems.

- Military radars that need to detect a large number of targets at high velocity use phased array antennas.

- Space communication between satellites or between a satellite and a probe.


