This post’s subject is high voltage transmission in direct current (HVDC). It explained the reason for using this transmission method.
The system
Most of an electrical energy transmission and distribution system uses alternate current (AC). However, some parts of the system use high voltage direct current transmission. (HVDC).
Advantages and disadvantages
Why use HVDC?
- Transmission by HVDC uses only two cables, one for the positive pole and another for the negative pole. While high voltage transmission by alternate current (HVAC) requires 4 conductors, due to three-phase transmission. In the post, whose link is below, shows the reason for using three phases.
Why is the system three-phase?Click here
- Transmission by DC does not produce skin effect, because there is no change in electric current’s direction. Therefore, it’s a more efficient transmission.
- There is no reactive power.
- It can make connections between power systems with different frequencies, it’s called asynchronous connection.
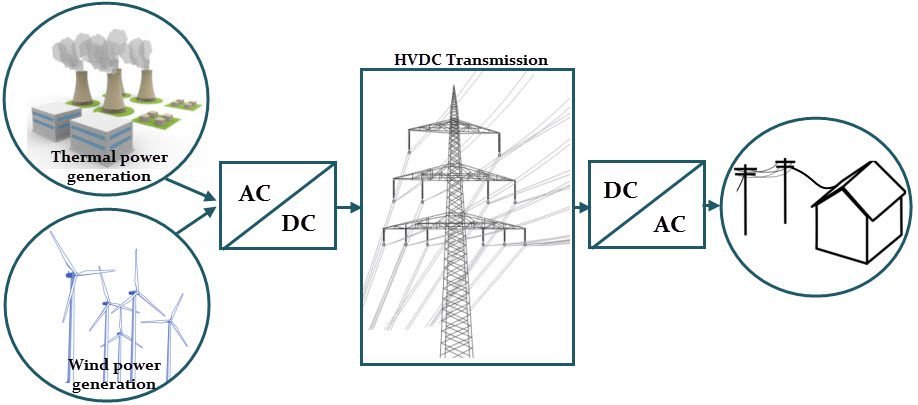
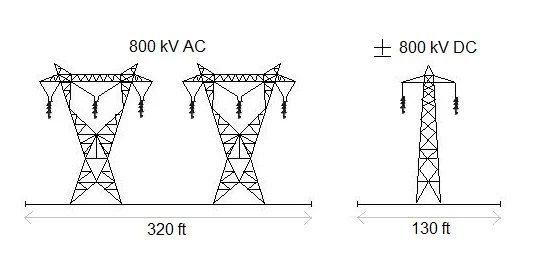
- Transmission towers occupy less space, reducing cost.
Also has disadvantages, such as:
- Additional cost due to rectifiers and inverters installations, to make conversion.
- On alternate current, transformers are necessary to increase voltage, to minimize losses by voltage drop and to decrease the voltage, to be distributed among consumers. However, transformers can’t increase or decrease direct voltage.
When using HVDC?
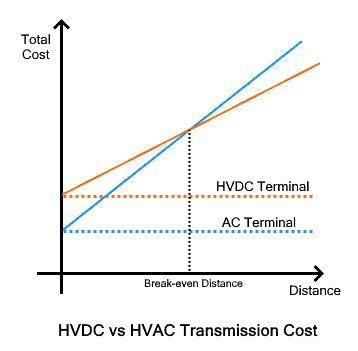
Transmission by direct current is economically viable when the distance of transmission lines is higher than the break-even distance, which is between 600 and 800 km (372 and 497 miles) for overhead lines and, between 50 and 100 km (31 and 62 miles) for underground cables.


