The boolean theorems are a set of rules from boolean algebra to simplify logic expressions of combinational circuits.
Post about combinational circuitsClick here
Boolean algebra is a fundamental mathematical tool for digital computing, where variables and functions have only binary values of “0” or “1”. It was introduced in 1854 by the British mathematician George Boole. In this algebra, the add signal (+) represents the logical operation OR and the multiplier signal (\times ou \cdot) represents the logical operation AND.
Boolean theorems with one variable
Every variable is represented by a letter; this variable’s negation is usually represented by a bar above the letter. For example, \overline{A} is the negation of A, therefore, \overline{A} will always have the opposite binary value of A. This is the list of theorems with only one variable.
- A+0=A
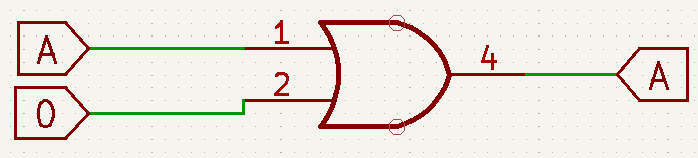
- A+1=1
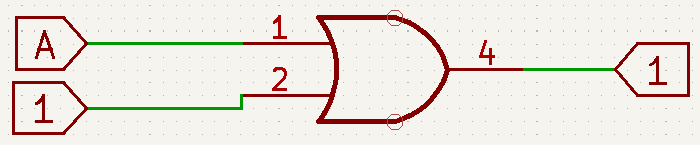
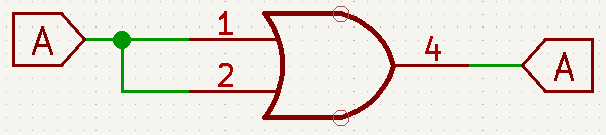
- A+A=A
- A+\overline{A}=1
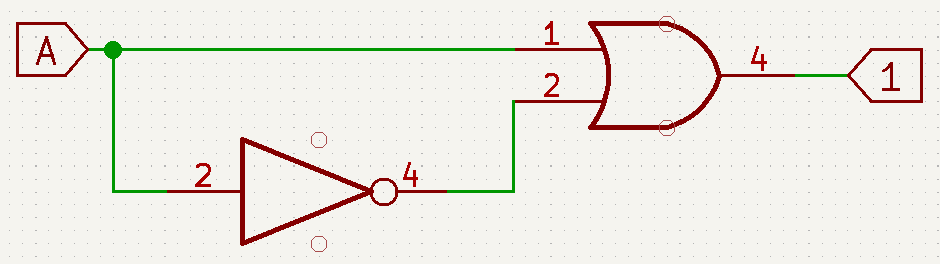
- A\cdot 0=0
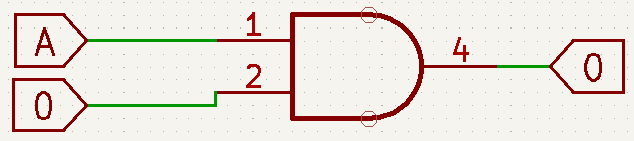
- A\cdot 1=A

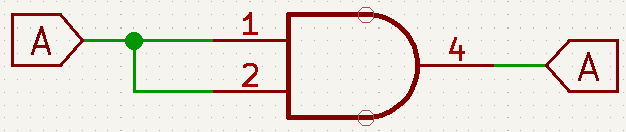
- A\cdot A=A
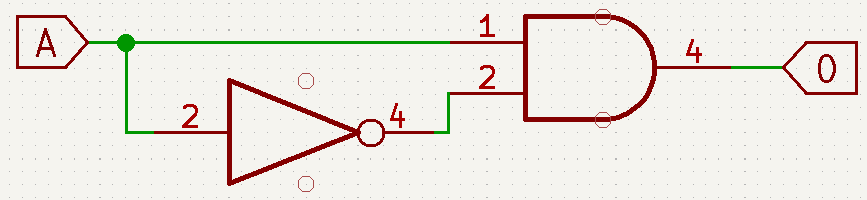
- A\cdot\overline{A}=0
Boolean theorems with two or three variables
- A+B=B+A
- A\cdot B=B\cdot A
- A+(B+C)=(A+B)+C=A+B+C
- A(BC)=(AB)C=ABC
- A(B+C)=AB+AC
- (A+B)(C+D)=AC+AD+BC+BD
- A+AB=A
- A+\overline{A}B=A+B
- \overline{A}+AB=\overline{A}+B
De Morgan theorems
These are very useful in manipulation of logical expressions.
\overline{(A+B)}=\overline{A}\cdot \overline{B}
\overline{(A\cdot B)}=\overline{A}+\overline{B}
Proving De Morgan theorems with a truth table and considering all possibilities.
\overline{(A+B)}=\overline{A}\cdot \overline{B}
A B A+B \overline{(A+B)} \overline{A} \overline{B} \overline{A}\cdot \overline{B} 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
\overline{(A\cdot B)}=\overline{A}+\overline{B}
A B A\cdot B \overline{(A\cdot B)} \overline{A} \overline{B} \overline{A}+\overline{B} 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
For what serves the boolean theorems?
With these theorems, combinational circuits can be simplified to have only one type of logic door such as NAND or NOR, since commercial integrated circuits with logic door uses only a type of door.