The Crookes radiometer, or light mill, it’s an experiment which demonstrate motion caused by electromagnetic radiation.
Theories about the operation of Crookes radiometer
Although it was invented in 1873, by the British physicist and chemistry Sir William Crookes, until today the operation of this experiment is debatable. The Crookes radiometer consists in a glass bulb, whose inside, has partial vacuum and four vanes equidistants from each other and made of light mica. In each one of these vanes, there is a white or silver side and a black side. The vanes’s black side absorbs more electromagnetic radiation than the lighter side. Therefore, the thin air on the black side has higher temperature.
Theory of motion caused by air heating
Many sources claim that air heating on vane’s black side causes a pressure increase in air pressure, resulting in vane’s motion.
According to Lunazzi and De Souza, 2021), on article “O radiômetro de Crookes é um cata-luz” (Crookes radiometer is a light mill), heat dissipates through bulb’s walls. After the vane completes a turn, it reaches the thermal balance and can receive more heat from an external source.
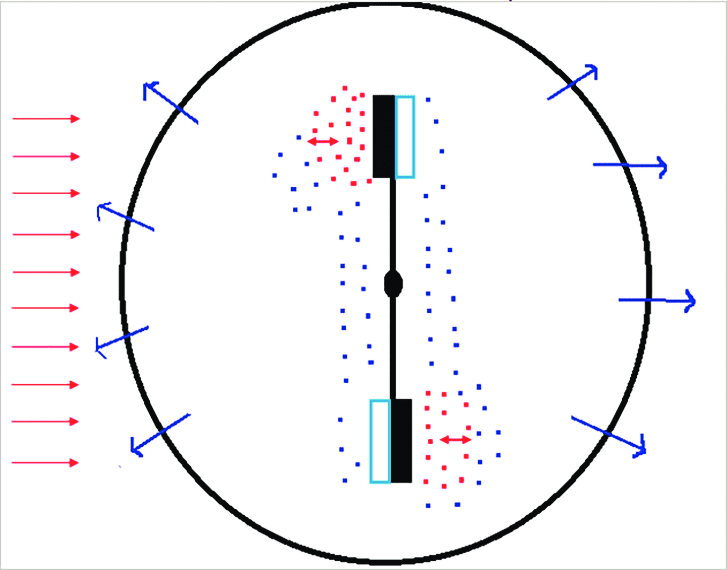
If the vanes where in total vacuum, there wouldn’t be air to generate pressure to spin. On the other hand, if it were filled with air and no vacuum, it would have too high air resistance to oppose vanes’ motion.
Jerry Liu theory
In a recent article, published by Jerry Z. Liu, from Stanford University, claims that the molecules close to the black side not only collide with the vane, but also with other air molecules, preventing them to get close to the vane. Therefore, pressure difference can’t be tha cause of motion, because the resulting force would be the same of air pressure.
When an atom absorbs energy from a photon, light particle, an electron from valence shell goes to an orbit with higher energy. After this absorption, appears a repulsion force between the atom which absorbed the electron and the neighboring atoms. According to the article, this force can be responsible for the Brownian motion and take part on physical state transition. The link for the article is here.