The maglev is a type of train that uses electromagnetism to levitate above rails, eliminating friction. But how does it work? Let’s find out in this post.
Category: Magnetism
Capacitance and inductance: more information
I received requests to write more about capacitance and inductance. This post can be considered as the second part of derivated electrical quantities.
Electromagnetic pulse (EMP)
I received requests to write about electromagnetic pulse (EMP). In this post, are described the power of EMP, source, and weapons which use this technology.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI)
Fulfilling requests, this post’s subject is the problem of electromagnetic interference (EMI). In addition to relation with electromagnetic compatibility.
Electrical e-Library at CERN (Part 2)
Continuing the visit to CERN. This second and last part is about the permanent exhibition of Microcosm and the guided tour.
Electrical e-Library at CERN (Part 1)
I was in Geneva, Switzerland, and I visited the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN). This site shows permanent exhibition for visitors.
Technical Museum Nikola Tesla (Part 1)
I was in Zagreb, Croatia’s capital and visited the Technical Museum Nikola Tesla. It is a huge museum and this is the first part of series.
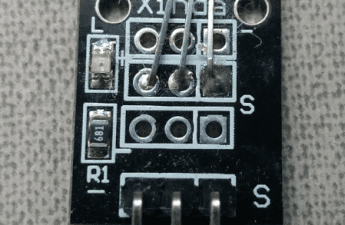
Hall effect: Operation and sensor
Today are shown how Hall effect works, a magnetic sensor using this phenomena and how o use it in projects with Arduino.
Asynchronous x synchronous generators
This post is about a comparison between asynchronous and synchronous generators. Showing main advantages and disadvantages of both.
How asynchronous generator works?
The asynchronous generator is also called induction generator. It is used in small hydropower plants and wind turbines.