This is the second part of antennas. Will be shown other parameters and some types of antennas.
Click here to see the first part.
Other parameters
- Front-back rate (FBR): Is the rate between radiated energy in the main direction of antenna propagation P_{m} and the energy in the opposite direction P_{op}.
FBR=\frac{P_{m}}{P_{op}}
FBR(dB)=10log(\frac{P_{m}}{P_{op}})
The bigger lobule in the radiation diagram always stays in main direction of propagation.

- Aperture efficiency: is the relation between the effective area A_{eff} and the physical area A_{p}. Effective area is the rate between received power by the antenna P_{T} and density of incident power W_{i}.
\varepsilon _{A}=\frac{A_{eff}}{A_{p}}
A_{eff}=\frac{P_{T}}{W_{i}}
Space around the antenna is divided in three fields:
- Near field reactive: This is the region dominated by non-radiating or reactive fields. The electric and magnetic fields are out of phase 90º from each other due to the antenna’s inductive and capacitive effects. R is the distance from antenna, D is the antenna’s diameter or length and \lambda is the wavelength.
R<0,62\sqrt{\frac{D^{3}}{\lambda }}
To small antennas in relation to wavelength, the approximation of near field reactive boundary is shown in the equation below.
R<\frac{\lambda }{2\pi }
- Fresnel or near radiative field: This is the transition between reactive and radiative fields. In this region, the radiation pattern changes with distance. This is the distance band.
0,62\sqrt{\frac{D^{3}}{\lambda }}<R<2\frac{D^{2}}{\lambda }
- Far field: Dominated by radiative field, electric and magnetic fields are in phase.
R>2\frac{D^{2}}{\lambda }

Cloverleaf and helix antennas
Exist many types of antennas, in this post, I will explain these two types. This is the Cloverleaf antenna, which can have 3 or 4 petals or wire loops.
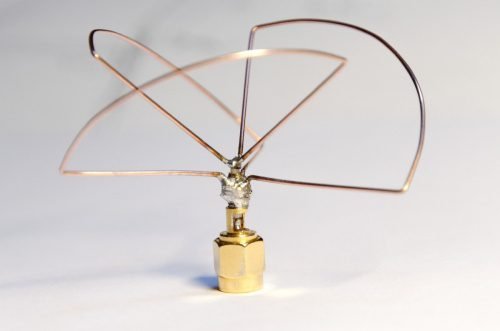
It is an omnidirectional antenna with circular polarization and its radiation pattern is similar to the dipole. Has low gain and it is better to transmission than reception. This antenna`s diameter is half of the wavelength.

The Cloverleaf antennas are used in MIMO systems and communication with drones. Below is the helix antenna.

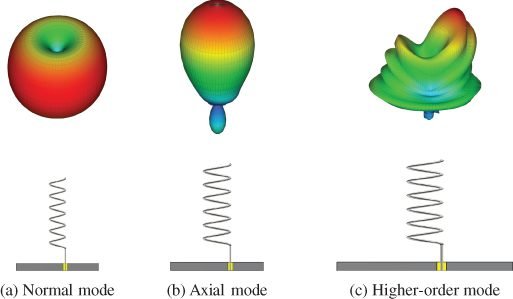
As a directional antenna, the spiral wire produces a circularly polarized wave.

Has a wide frequency band and it is easy to build, however, the efficiency decreases with the increasing number of turns. The radiation pattern depends on the antenna’s dimensions. When the antenna’s diameter is small compared with the wavelength, the pattern is normal (a). When the dimensions are bigger than necessary to pattern (b), occurs the mode (c).
Are used in HF and VHF and satellite communication, like this array of helix antennas.

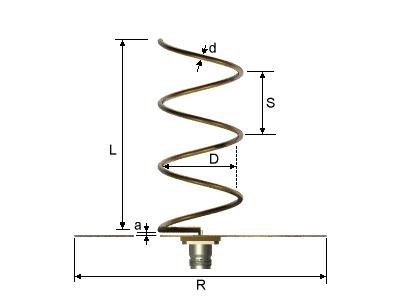
The pitch angle determines this antenna’s dimensions and it is calculated this way.
\alpha =tan^{-1}\frac{S}{\pi D}
In the next post on telecommunications, I will talk about the other types of antennas.


