Graphene is still too expensive and difficult to make on large scale. While graphene oxide is a graphite derivate, which is cheaper and easier to manufacture.
It recommendable to read the post about graphene before continuing.
Graphene’s properties and informationClick here
Composition and properties
Graphene oxide is composed by a graphene layer and carboxyl (COOH), carbonyl (CO), hydroxyl (OH) and epoxy (1 oxygen atom with 2 simple covalent bonds with 2 carbon atoms) groups.
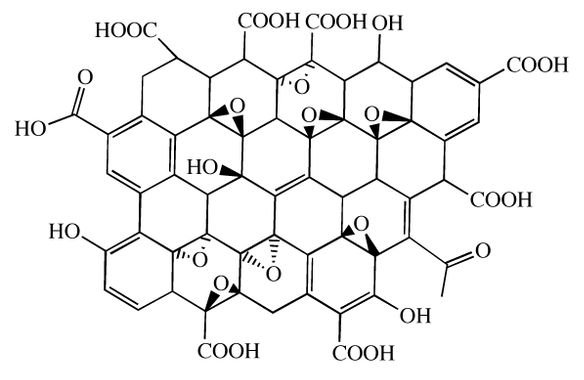
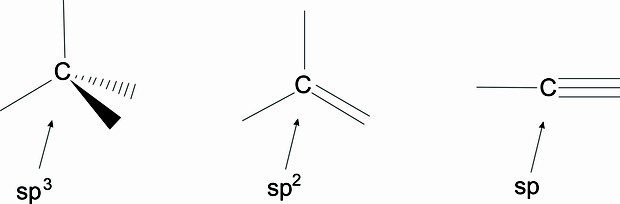
Graphene oxide is hydrophilic and easily dispersible in water and in many other solvents, due to ionizable border with carboxyl groups. This material is electrically insulant, in opposition to pure graphene, due to the presence of hydroxyls and peroxides, the later make some carbon atoms have sp³ hybridization.
Graphite is oxidated and then passes through an exfoliation process and, graphene oxide is produced. More details will be explained in another post.
Some applications of graphene oxide
Water desalinization
The graphene oxide (GO) can be used to make seawater drinkable, 97% of salt is filtrated. Layers of GO are put together, distances between membranes must allow passage of water molecules and stop ions.
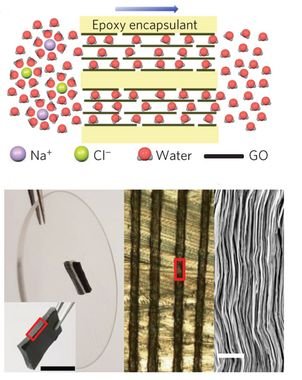
In addition to that, covalent bonds between ion and water molecules, are stronger than hydrogen bridges, which link water molecules. Therefore, hydrogen bridges can be broken for water to pass through the filter.
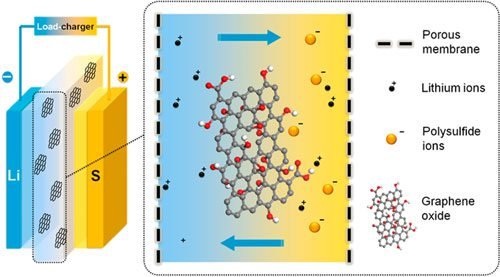
Batteries
GO membranes can be used as a separator, to increase the stability of lithium-sulfur batteries. This type of battery theoretically has more energy density than the popular Li-ion. In addition to sulfur be a very abundant element on Earth.
Reduced graphene oxide
When graphene oxide passes through a reduction process, it becomes reduced graphene oxide. The later has less organic groups.

This material is a conductor. although not as much as pure graphene. The reduction can be chemical, thermal, or electrochemical.
Some application examples
Thin film transistors
The rGO can serve as electrodes and channels in thin film transistors (TFT), due to flexibility. Transistors made exclusively of rGO can be bent more than 10,000 times without losing conductivity. Besides being cheaper than TFT with graphene.

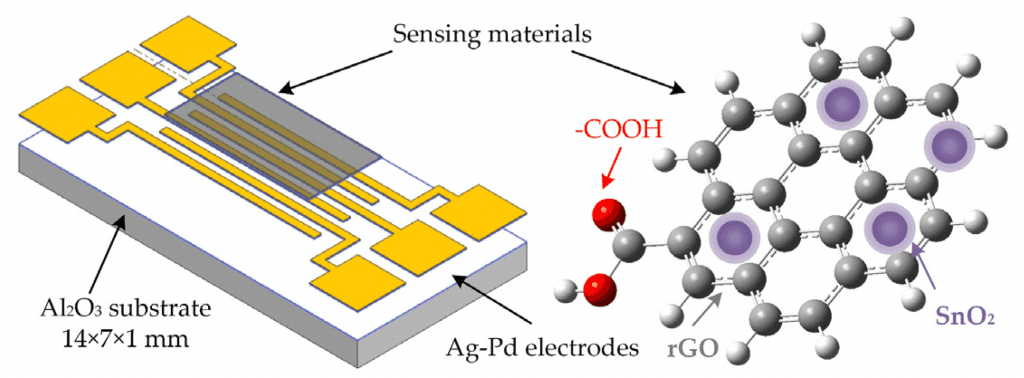
Sensors
The groups with oxygen in rGO allow that material to absorb gas molecules. Therefore, field effect transistors with an rGO membrane between its electrodes can be a very sensitive electrochemical gas sensor. It is also capable to detect organic molecules, depending on the substrate and combination with other materials.