In this post I will talk about diodes which are semiconductors components which make the current flow in only one direction.
News: Sunglasses can generate energy
A sunglasses uses organic solar panels in lens to produce electrical energy.
What is WiMAX?
In this post I will explain what is WiMAX. WiMAX means Wordwide Interoperability for Microwave Acess, is a technology which follows the IEEE 802.16 standard to wireless communications to provide fixed and mobile broad band internet.
Features
Some WiMAX features:
- 6 to 9 Km range, vary with obstacles;
- Can be used when is not viable to install cable or optics fibers;
- Since it follows the IEEE 802.16 standard, operate in 2 to 10 GHz;
- Provide internet and telephone access, data and voice transfer;
- 70 Mbps speed;
- User and base station don’t need to stay in visible range.
Architecture
This is the IP based WiMAX architecture:

MS are mobile stations which are consumer’s smartphones, tablets, PC. ASN is Access Service Network composed by base stations which function is provide interface to mobile stations, ASN Gateway (GW) is an aggregation traffic layer and form the radio access network. CSN provides connection with the internet, ASP, private and public networks.
AAA means Authentication, Authorization and Accounting server; used to services which demand subscription, PSTN is public telephone network, OSS/BSS are operation system support and business operation system, 3GPP/3GPP2 are third generation standard, MIP-HA is Mobile IP Home Agent which is a router to keep information about the device’s location.
Infrastructure
This figure shows the architecture with device’s representations.

Since WiMAX has a bigger range than WiFi, it needs more powerful transceivers. Here is a directional antenna WiMAX model PA-3500.

WiMAX towers use the same principle of cellphones, a WiMAX tower below.


WiMAX receivers to users.

What is spintronics?
This post will bring an introduction to spintronics. While electronics manipulate the electrons’ movement, spintronics is the engineering field that manipulates the movement and spin of electrons. The electron spin can assume two values: spin-up (anticlockwise) and spin-down (clockwise).
Optical fibers: Operation, types and how to made
Optical fibers are a very fast way to send information via light, it can transmit at speed until 100Mps (Megabits per second), has immunity against electromagnetic interference, low weight, and loss of signal. I will explain how optical fibers work and how they are made.
How photovoltaic solar panels work? (Part 2)
This is the second part of photovoltaic solar panels topic.
Solar panel positioning
To obtain maximum energy production, the photovoltaic module must be positioned considering Earth’s rotation inclination axis, latitude, and Sun’s azimuthal angle. To receive maximum energy daily, the module must always be appointed to geographic north and the inclination angle must be adjusted in relation to the soil.
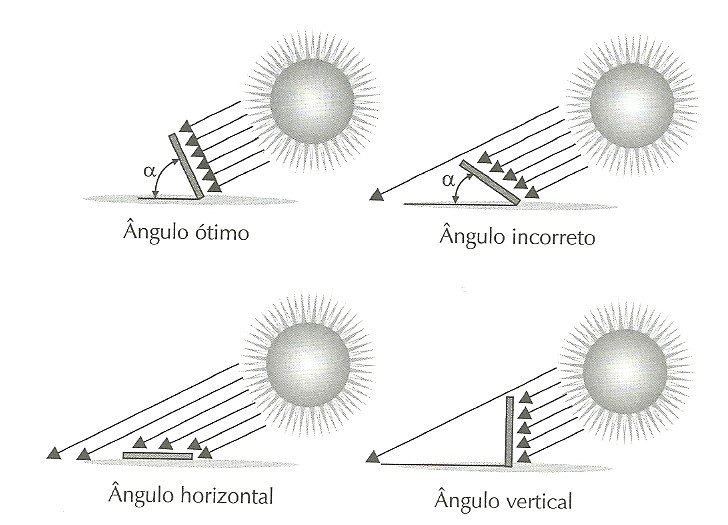
Inclination angle depends on the altitude.
Considerate the solar panel model:
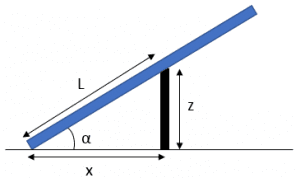
The equation to calculate height stem z:
z=L\cdot sen\alpha
To calculate the distance x:
x=L\cdot cos\alpha
To build solar panels parallel rows, it is necessary leave a distance d between the rows which is calculated in the following way:
d=3,5\cdot z
Characteristic curve
Here are the examples of characteristic curves of a solar panel. The black curve is the current-tension (I-V) characteristic curve and the green curve is the power-tension curve (P-V). Note the red dot which is the Maximum Power Point. All solar panels follow this pattern curve. Usually, these curves are provided by the manufacturer.
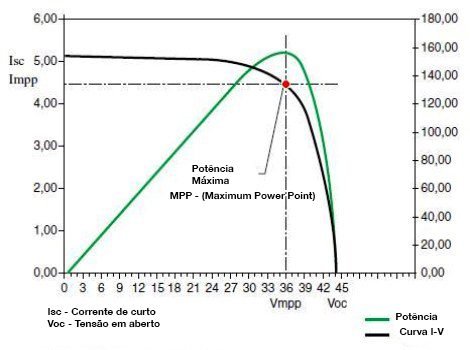
Temperature and solar radiation also influence the curve. Influence by solar radiation:
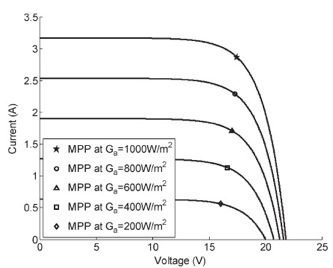
Influence by temperature:
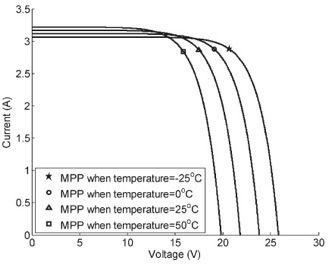
Materials for photovoltaic cells
There are various materials to build photovoltaic modules, usually, the material is silicon, however, there are various types of silicon and other materials.
- Monocrystalline silicon

The monocrystalline silicon has a homogeneous molecular structure, here is the final product of monocrystalline cell.

Those types of cells are the most efficient actually, but have a high cost and need to be installed in modules to obtain mechanical resistance. The manufacturing process waste big parts of silicon.
- Polycrystalline silicon

This silicon type has many crystals with different shapes and sizes in the molecular structure. Here is a solar cell made with this material.

The manufacturing cost of this material is lower and produces less silicon waste, but efficiency is a bit lower compared with monocrystalline due to low purity. Also needs to be installed in modules for mechanical protection.
- Thin film formless silicon

Used more for small applications, cells with this material have low efficiency. Its efficiency decrease in 6 or 12 months due to degradation caused by light until reaches a stable value. The efficiency can be increased with stacking, a technique to put many formless silicon layers, however, the technique’s cost is high.
- Thin film of cadmium telluride (CdTe)

Cells with this material have the best cost/efficiency ratio between the thin film panel, are used in large solar power plants. It is not produced on a large scale because cadmium is toxic and tellurium is a rare material.
- Thin film of copper selenite, indium and gallium (GICS)

It has the highest efficiency between the thin film solar cells, however, are still very expensive.
- Hybrid cells

It was searched to combine the high efficiency of crystalline cells with the thin film’s lower cost. There is no efficiency degradation due to light and works well with high temperatures.
Efficiency table
Here is a table to compare efficiency between cells and modules for different materials.
| Material | Efficiency cell in laboratory | Commercial cell efficiency | Commercial module efficiency |
| Si monocrystalline | 24,7% | 18% | 14% |
| Si polycrystalline | 19,8% | 15% | 13% |
| Si formless | 13% | 10,5% | 7,5% |
| CdTe | 16,4% | 10% | 9% |
| GICS | 18,8% | 14% | 10% |
| Hybrid | 20,1% | 17,3% | 15,2% |
News: AI visualize 3D objects from 2D pictures
Visualize 3D objects from 2D photos was exclusivity of humans, now an algorithm can do it.
Source: Science
They started by teaching an algorithm to treat 3D objects as 2D surfaces. Imagine, for example, hollowing out a mountainous globe and flattening it into a rectangular map, with each point on the surface displaying latitude, longitude, and altitude. After much practice, the new machine-learning algorithm learned to translate photos of 3D objects (like the first row of planes, above) into 2D surfaces, which can then be “stitched” into 3D forms. Researchers trained it to reconstruct cars, airplanes, and hands in almost any posture.
This program called SurfNet can create 3D images of cars, aircrafts and hands. Need to create an algorithm which estimate 3D form of any object even the ones it never saw and wasn’t trained.
The integrated circuit 555
I will explain how the 555 IC (Integrated circuit) works and what you can do with it. This is one of the most useful components you can use in your personal projects.
Stepper motors
In this post, I will explain how stepper motors works. Stepper motors are motors which spin on steps due to activation of coils in the stator. This type of motor has many input wires to turn on a specific coil.










